9 things to know before you get Leg-Lengthening Surgery

Considering leg-lengthening surgery is a significant decision that can have a transformative impact on your life. Dr. Sarin, a distinguished figure in orthopedic surgery, offers invaluable expertise in the realm of leg lengthening procedures. Before taking this life-altering step, it’s crucial to be well-informed about the process. Here are nine essential factors to consider. Conclusion Choosing to undergo Leg Lengthening Surgery is a significant step towards achieving the height you desire. Dr. Sarin’s expertise, combined with a personalized approach, ensures that you are in capable hands throughout the process. With thorough pre-operative evaluation, advanced surgical techniques, and comprehensive post-operative care, Dr. Sarin and his team offer a pathway to a taller, more confident you. Take the time to explore this transformative option and make an informed decision for your future. Also Read: Can Height Surgery Help You Get Taller? How much Height can be Increased by Surgery Best Diet for Bone Healing After Limb Lengthening How We Help You Return to Work and Sports After Limb Lengthening? How to Lengthen Legs Naturally & Surgically in 2025
What are the Long-Term Effects of Bone Lengthening?
Bone lengthening, such as the innovative procedures offered by Dr. Sarin, can be a life-changing solution for individuals seeking to increase their height or address limb length discrepancies. While the short-term benefits are evident, it’s crucial to consider the long-term effects of such surgeries. Here, we delve into the lasting outcomes and considerations associated with Dr. Sarin’s surgery: 1. Enhanced Quality of Life: One of the most significant long-term effects is the potential for an enhanced quality of life. Dr. Sarin can correct issues like limb length discrepancies, leading to improved mobility, comfort, and overall well-being. 2. Continued Healing and Adaptation: After the surgery, the lengthened bones continue to heal and adapt over time. This process involves the gradual formation of new bone tissue, ensuring the stability and durability of the lengthened limbs. 3. Improved Self-Esteem: Long-term, patients often report improved self-esteem and confidence. Achieving the desired height or limb symmetry can have a lasting positive impact on self-perception and mental health. 4. Commitment to Physical Therapy: Successful long-term outcomes often depend on a commitment to post-surgery physical therapy. Dr. Sarin’s team provides guidance and support to ensure patients achieve optimal results. 5. Potential for Future Surgeries: While leg lengthening surgery can be transformative, it’s essential to consider potential future surgeries or adjustments. Some patients may choose additional procedures for further enhancement. 6. Comprehensive Follow-Up Care: Dr. Sarin and his team prioritize comprehensive follow-up care to monitor the long-term effects of the surgery. Regular check-ups and assessments are crucial to ensuring ongoing success and addressing any issues that may arise. 7. Personalized Results: The long-term effects can vary from one patient to another, depending on factors such as individual healing, compliance with post-operative care, and the specific goals of the surgery. Dr. Sarin’s approach is highly personalized to achieve the best possible outcomes for each patient. Dr. Sarin offers the potential for transformative long-term effects, including improved quality of life, enhanced self-esteem, and continued healing and adaptation. While the procedure can be life-changing, patients need to commit to post-operative care and follow-up appointments to ensure the best possible results. Dr. Sarin and his team are dedicated to providing exceptional care and support throughout the entire journey, from surgery to long-term recovery. Also Read: 9 things to know before you get Leg-Lengthening Surgery Can Height Surgery Help You Get Taller? How much Height can be Increased by Surgery Best Diet for Bone Healing After Limb Lengthening How We Help You Return to Work and Sports After Limb Lengthening?
Optimum Muscle Form and Weight for Limb-Lengthening

It is a groundbreaking procedure that can significantly improve the lives of individuals seeking to address limb length discrepancies or achieve their desired height. However, achieving the best possible outcomes involves more than just the surgical aspect; it also entails optimizing muscle form and weight. Here, we delve into the crucial considerations for achieving the ideal muscle form and weight during and after Dr. Sarin’s surgery: 1. Balancing Muscle Development: Achieving the optimum muscle form during surgery involves a delicate balance. Dr. Sarin’s surgical techniques are designed to minimize muscle disruption, allowing for better preservation of muscle function. 2. Post-Surgery Physical Therapy: Following surgery, a comprehensive physical therapy regimen is crucial. It helps patients regain strength, flexibility, and muscle tone. Dr. Sarin’s team provides tailored physical therapy plans to ensure optimal muscle recovery. 3. Monitoring Muscle Development: Throughout the limb lengthening process, Dr. Sarin and his team closely monitor muscle development. This ensures that the lengthening process does not compromise muscle health and function. 4. Nutrition and Weight Management: Maintaining an appropriate weight and balanced nutrition is essential for achieving optimum muscle form. Dr. Sarin’s team guides nutrition and weight management to support muscle health. 5. Individualized Approaches: Dr. Sarin’s approach is highly individualized. He takes into account each patient’s unique physique, limb length goals, and muscle structure to create a customized surgical plan that minimizes muscle disruption. 6. Long-Term Muscle Health: Achieving the desired limb length is just the beginning. Dr. Sarin’s emphasis on long-term muscle health ensures that patients not only reach their goals but also maintain muscle strength and function for years to come. 7. Patient Commitment: Achieving optimum muscle form and weight for limb lengthening surgery requires commitment from the patient. Following the recommended post-operative care and physical therapy is vital for long-term success. Dr. Sarin’s surgery is not only about achieving the desired limb length but also about optimizing muscle form and weight for overall well-being. The careful balance of surgical techniques, post-operative care, physical therapy, and individualized approaches ensures that patients can enjoy the best possible outcomes while maintaining muscle health and function. Dr. Sarin and his team are dedicated to providing comprehensive care throughout the entire limb-lengthening journey, from surgery to long-term recovery. Also Read: What are the Long-Term Effects of Bone Lengthening? 9 things to know before you get Leg-Lengthening Surgery Can Height Surgery Help You Get Taller? How much Height can be Increased by Surgery Best Diet for Bone Healing After Limb Lengthening
Bone Healing After Leg Lengthening Surgery
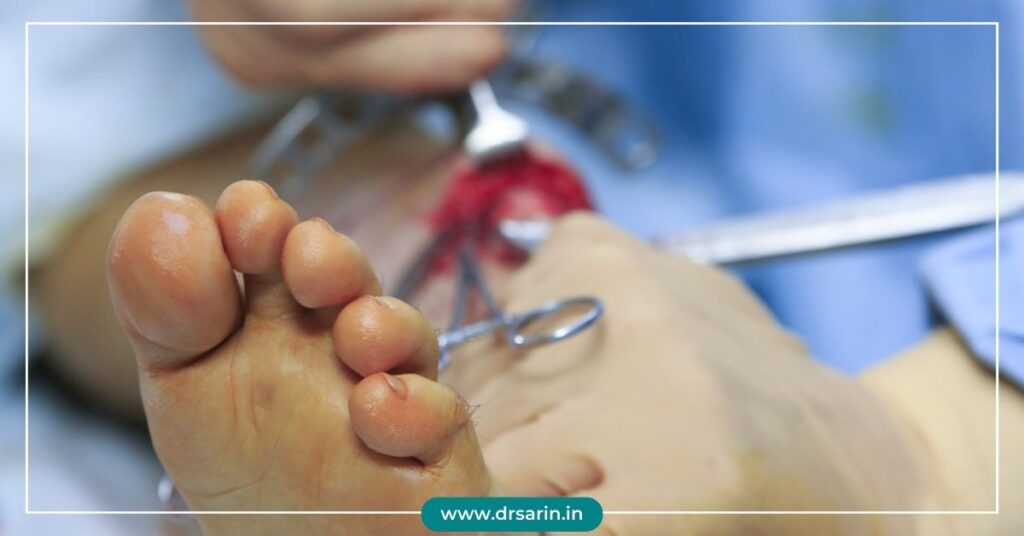
Leg lengthening surgery, a medical procedure designed to increase a person’s height, is a complex and intricate process that involves the elongation of bones in the lower limbs. This surgery is typically chosen by individuals who seek to gain a few inches in height or correct limb length discrepancies. While leg lengthening surgery can be life-changing, it’s crucial to understand the bone healing process that follows this procedure to ensure a successful outcome. The Basics of Leg-Lengthening Surgery Leg lengthening surgery, also known as limb lengthening, is performed by orthopedic surgeons to increase the length of the bones in the legs. This surgery involves external fixation devices, such as the Ilizarov apparatus or the newer Taylor Spatial Frame. These devices are attached to the bones with pins or wires, allowing controlled separation of bone segments. During the surgery, the bone is intentionally broken in a controlled manner, creating a gap between the bone segments. Over time, the body’s natural healing mechanisms work to bridge this gap with new bone formation. To assist in this process, the external fixator devices are adjusted regularly to encourage gradual bone growth. Bone Healing Stages The bone healing process after leg lengthening surgery typically follows these key stages: 1. Inflammatory Phase: Immediately after surgery, the body responds with inflammation. This phase is crucial for bringing essential nutrients and cells to the site of the bone gap. 2. Soft Callus Formation: Over the next few weeks, a soft callus forms around the bone gap. This initial tissue is a mixture of collagen and cartilage. 3. Hard Callus Formation: As the weeks progress, the soft callus gradually transforms into a hard callus composed of new bone tissue. This process is known as endochondral ossification. 4. Consolidation Phase: The bone continues strengthening, and the external fixator devices are periodically adjusted to maintain the desired bone length. This phase can last several months, depending on the extent of the lengthening. 5. Final Remodeling: After the consolidation phase, the bone undergoes further remodeling, aligning itself into a more natural, uniform structure. This process can continue for several years, although patients typically regain total weight-bearing capacity much earlier. Factors Affecting Bone Healing Several factors can influence the bone healing process after leg lengthening surgery, including: Patient’s Age: Younger patients tend to experience faster bone healing. Overall Health: Nutritional status, underlying medical conditions, and smoking habits can impact bone healing. Surgical Technique: The surgeon’s experience and technique can influence the procedure’s success. Compliance: Following post-surgery care and adjustment instructions is vital for successful bone healing. Conclusion Limb lengthening surgery is a life-changing procedure that can enhance a person’s height and correct limb length discrepancies. Understanding the bone healing process is essential for patients and healthcare providers involved in this journey. While the bone healing stages can be challenging and require patience, the ultimate goal is to achieve a more balanced and harmonious physique. With the guidance of experienced medical professionals and a commitment to post-surgery care, successful bone healing can lead to a brighter, taller future for those who choose this transformative surgery. Also Read: Determining Age Limits for Leg Lengthening Surgery External Methods vs. Internal Methods of Cosmetic Leg Lengthening Should Limb Lengthening Surgery be left or Continued? Height Increase Surgery: Purpose, Procedure, and Benefits and Side Effects 5 Common Questions About Limb Lengthening
Reasons Why People Get Cosmetic Leg-Lengthening Surgery Done

In recent years, an intriguing trend has emerged in cosmetic procedures: leg-lengthening surgery. This groundbreaking procedure, offered by esteemed professionals like Dr. Sarin, has piqued the interest of individuals seeking to enhance their stature. Understanding the motivations behind this transformative surgery sheds light on why people undergo such a procedure. 1. Height Empowerment Height has long been associated with confidence and perceived social advantages. For some individuals, achieving a taller stature through leg-lengthening surgery serves as a means to enhance self-esteem and confidence. Dr. Sarin’s expertise in this field allows patients to address their insecurities and gain newfound confidence by altering their physical appearance. 2. Corrective Measures Beyond cosmetic aspirations, there are cases where individuals seek leg-lengthening surgery for corrective purposes. Congenital conditions, injuries, or leg length discrepancies often lead people to consider this surgical option. Dr. Sarin’s specialized approach caters to cosmetic enhancements and addresses medical concerns, ensuring comprehensive care for patients seeking corrective measures. 3. Professional and Social Advantages Height is sometimes associated with societal advantages, especially in certain professions or social settings. Some individuals opt for leg-lengthening surgery as they believe it can positively impact their career prospects or social interactions. Dr. Sarin’s expertise in understanding these nuanced motivations ensures that patients receive personalized consultations, acknowledging their unique aspirations and goals. 4. Psychological Well-Being The psychological impact of one’s appearance cannot be understated. For many, the decision to undergo leg-lengthening surgery is deeply rooted in their desire for psychological well-being. Dr. Sarin’s compassionate approach to guiding patients through this transformative journey encompasses physical, emotional, and mental aspects, ensuring a holistic experience. 5. Sarin’s Expertise In Leg-Lengthening Surgery Dr. Sarin stands at the forefront of this specialized field and is renowned for expertise, precision, and patient-centered care. His commitment to utilizing cutting-edge techniques and prioritizing patient safety has earned him a stellar reputation in cosmetic leg-lengthening surgery. The Importance of Informed Decisions Dr. Sarin’s practice prioritizes patient education and informed decision-making. He ensures that individuals considering leg-lengthening surgery are well-informed about the procedure, its potential risks, and the realistic outcomes. This approach empowers patients to make confident choices about their transformative journey. Conclusion The motivations driving individuals to pursue cosmetic limb lengthening surgery are multifaceted and deeply personal. Dr. Sarin’s expertise caters to the physical aspects of this procedure and acknowledges and supports the diverse motivations behind each patient’s decision. By offering personalized care, guidance, and expertise, Dr. Sarin continues to redefine the landscape of cosmetic leg-lengthening surgery, empowering individuals to embrace their desired transformations confidently. Also Read: Does Limb lengthening surgery have any downsides? Limb Lengthening History Understanding the Phases of Limb Lengthening Bone Healing After Leg Lengthening Surgery Determining Age Limits for Leg Lengthening Surgery
Should Limb Lengthening Surgery be left or Continued?

Limb lengthening surgery is a medical procedure that has gained attention for its potential to enhance the stature of individuals who desire it. Dr. Sarin, a renowned expert in the field, has been at the forefront of limb surgery, providing guidance to patients facing the critical decision of whether to continue or discontinue the procedure. The Controversy of Limb-Lengthening Surgery It is a complex and lengthy process that involves the gradual extension of the bones in the legs. While it can fulfil the aesthetic and psychological needs of some patients, it is not without controversy. Before making the decision to continue or halt limb-lengthening surgery, it’s crucial to consider several factors: 1. Medical Indications: Dr. Sarin emphasizes that limb surgery should primarily be considered for individuals with medical indications such as limb length discrepancies, dwarfism, or congenital conditions. It’s crucial to ensure that the procedure is medically warranted to minimize potential risks. 2. Psychological and Emotional Well-being: For some individuals, height plays a significant role in their self-esteem and confidence. Dr Sarin acknowledges the importance of addressing these emotional concerns but advises that patients should also seek psychological counselling to explore the underlying reasons for their desire to undergo the procedure. 3. Potential Risks and Complications: This surgery has risks. Patients must be aware of the potential complications, including infections, pain, and lengthy recovery periods. Dr. Sarin recommends thoroughly discussing these risks with a qualified medical professional before proceeding. 4. Patient Expectations: Dr. Sarin underscores the importance of setting realistic expectations. This surgery can add a few inches to a person’s height, but it is not a guarantee of transformational changes. Patients must have a clear understanding of what the procedure can and cannot achieve. 5. Ethical Considerations: Ethical concerns surround limb lengthening surgery, mainly when it is pursued solely for cosmetic reasons. Dr. Sarin encourages patients to reflect on their motivations and the ethical implications of their choices. In conclusion, the decision to continue or discontinue limb surgery is a deeply personal one, and it should be made with careful consideration of all factors involved. Dr. Sarin stresses the importance of seeking professional medical advice and psychological support throughout the decision-making process. While Limb Lengthening Surgery can be a viable option for some, it is crucial to prioritize the well-being and overall health of the individual. Ultimately, the choice should align with the patient’s physical and emotional needs while keeping safety and ethics at the forefront of the decision-making process. Also Read: Height Increase Surgery: Purpose, Procedure, and Benefits and Side Effects 5 Common Questions About Limb Lengthening What is Quadrilateral Lengthening? What is Quadrilateral Lengthening? Prejudice against Limb-Lengthening Surgery
Limb Lengthening History

The history of limb lengthening is a fascinating journey through medical innovation, perseverance, and the quest for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with limb length discrepancies or deformities. Let’s delve into the evolution of limb lengthening techniques and the milestones that have shaped this field. Ancient Beginnings: The roots of limb lengthening can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Historical records suggest that as early as the 8th century, methods such as traction and stretching were used in attempts to correct limb deformities. These early practices laid the foundation for the concept of gradual lengthening. Gavriil Ilizarov’s Groundbreaking Work: A major breakthrough in limb lengthening came in the mid-20th century with the pioneering work of Russian orthopedic surgeon Gavriil Ilizarov. In the 1950s, Ilizarov developed the Ilizarov apparatus, an external fixator that allowed controlled, gradual lengthening of bones. This revolutionary device transformed the field of orthopedics and became a cornerstone in limb lengthening procedures. Mechanical Advances: Advancements in the mechanical aspects of limb lengthening continued to evolve over the years. The introduction of motorized distraction devices in the late 20th century marked a significant improvement in the precision and ease of lengthening procedures. These devices allowed for more controlled adjustments and reduced the physical burden on patients. Modern Surgical Techniques: In the 21st century, limb lengthening procedures have become more sophisticated with the advent of minimally invasive surgical techniques. Precise imaging technologies, such as computerized tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), enable surgeons to plan and execute procedures with unprecedented accuracy. Distraction Osteogenesis in Orthopedics: Limb lengthening predominantly relies on a process known as distraction osteogenesis. This technique involves making a controlled osteotomy (bone cut) and gradually separating the bone fragments, stimulating new bone formation in the gap. It has proven effective in addressing various conditions, including congenital limb deficiencies, post-traumatic deformities, and discrepancies in leg lengths. Cosmetic Limb Lengthening: Beyond addressing medical conditions, limb lengthening has gained popularity for cosmetic purposes. In recent years, individuals seeking to enhance their height have undergone elective cosmetic limb lengthening procedures. This controversial practice has sparked ethical debates but highlights the versatility of limb lengthening techniques. The history of limb lengthening is a testament to the resilience of medical professionals in the face of challenges and their commitment to improving the lives of patients. From ancient methods to modern surgical innovations, this journey reflects the ever-evolving nature of medical science and the pursuit of solutions to enhance mobility and well-being. Also Read: Understanding the Phases of Limb Lengthening Bone Healing After Leg Lengthening Surgery Determining Age Limits for Leg Lengthening Surgery External Methods vs. Internal Methods of Cosmetic Leg Lengthening Should Limb Lengthening Surgery be left or Continued?
Determining Age Limits for Leg Lengthening Surgery
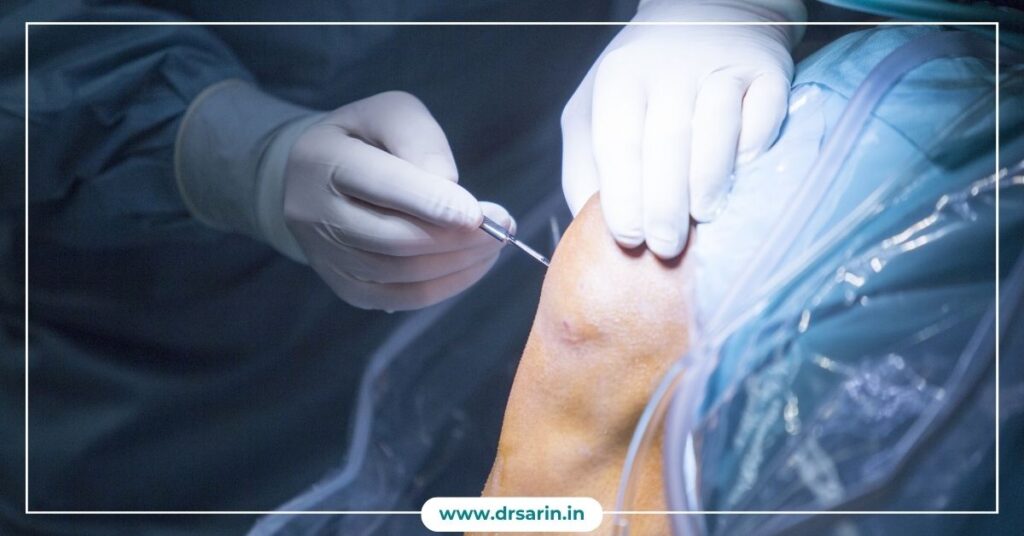
Leg lengthening surgery, a medical procedure that can increase an individual’s height, has become increasingly popular for those seeking to enhance their physical appearance or address medical conditions. However, the age at which one can undergo limb lengthening surgery is a crucial factor to consider. In this article, we will explore the age limits for leg lengthening surgery and the factors that play a role in determining the suitability of this procedure for different age groups. 1. Paediatric Patients: For children and adolescents with congenital conditions or growth plate injuries, limb surgery is typically considered an option. Pediatric orthopaedic surgeons assess the child’s growth potential and bone development before recommending the procedure. 2. Adolescents and Young Adults: In some cases, adolescents and young adults with growth discrepancies or deformities may be candidates for limb lengthening. The decision is often based on the individual’s physical and emotional readiness and the potential benefits of the surgery. 3. Adult Patients: While leg lengthening surgery is more commonly associated with growing individuals, some adults may still be eligible for the procedure. Factors such as bone density, overall health, and the reasons for seeking bone lengthening are carefully evaluated. 4. Age-Related Considerations: Bone Healing: The younger the patient, the better their bones tend to heal and adapt to the lengthening process. In children and adolescents, the bones are more malleable, making the procedure potentially more effective and with fewer complications. Psychological Readiness: For adolescents and adults, the psychological aspect of limb lengthening is a significant consideration. A thorough assessment of the patient’s emotional preparedness is essential. 5. Medical Indications vs. Cosmetic Reasons: Age limits can also vary depending on whether the surgery is being considered for medical reasons (e.g., addressing limb length discrepancies) or purely for cosmetic purposes. Medical indications may justify the procedure at different ages. 6. Consultation with Orthopaedic Specialists: Ultimately, the determination of age limits for leg lengthening surgery should be made in consultation with orthopaedic specialists who can assess the individual’s specific case, bone development, and overall health. 7. Risks and Benefits: It’s important for individuals considering this surgery to understand the potential risks and benefits, as well as the limitations of the procedure. The decision should be based on a thorough evaluation of individual circumstances. In conclusion, the age limits for limb surgery are not set in stone and can vary depending on the specific circumstances of each patient. Dr. Sarin and his team are dedicated to providing personalized care and expert guidance to patients considering limb lengthening surgery, ensuring the procedure is safe and effective. By consulting with Dr. Sarin, individuals can make informed decisions about the right time for their limb-lengthening journey, achieving the physical transformation and confidence they desire. Also Read: External Methods vs. Internal Methods of Cosmetic Leg Lengthening Should Limb Lengthening Surgery be left or Continued? Height Increase Surgery: Purpose, Procedure, and Benefits and Side Effects 5 Common Questions About Limb Lengthening What is Quadrilateral Lengthening?
Can You Do Sports after Limb Lengthening Surgery?

Limb lengthening surgery is a life-changing procedure that often raises questions about physical activity and sports participation during and after recovery. In this article, we’ll explore the factors that determine when and how individuals can safely return to sports following the surgery. Understanding Surgery This surgery is a specialized procedure designed to increase the length of bones, typically in the legs. Whether it’s for medical reasons, such as correcting limb length discrepancies or aesthetic purposes, the surgery involves gradually extending bones through a controlled process. As the bones lengthen, patients often wonder about the impact on their ability to participate in sports and physical activities. The Timing Matters One of the key factors in determining when you can resume sports after limb surgery is the timing of your return. It’s crucial to follow your surgeon’s advice and allow your body sufficient time to heal. The recovery process includes several stages: Consult with Your Surgeon It’s essential to have open communication with your surgeon throughout the process. They will assess your progress and determine when it’s safe for you to resume sports based on your individual recovery. Factors such as the type of sport you’re interested in, your overall health, and the specific details of your surgery will all influence their recommendations. Physical Conditioning is Key Before returning to sports, patients are advised to engage in conditioning exercises to ensure their bodies are prepared for the demands of physical activity. This step helps reduce the risk of injury and ensures a smoother transition back to sports. Conclusion While limb surgery can be a transformative experience, it’s essential to prioritize your health and safety throughout the recovery process. Resuming sports after limb surgery is possible, but it must be done gradually and under the guidance of your surgeon and physical therapist. Always consult with your medical team to make informed decisions about your return to sports, taking into account your unique circumstances and goals. Also Read: Body Proportions after Limb Lengthening Surgery Optimum Muscle Form and Weight for Limb-Lengthening What are the Long-Term Effects of Bone Lengthening? 9 things to know before you get Leg-Lengthening Surgery Can Height Surgery Help You Get Taller?
Understanding the Phases of Limb Lengthening with Dr. Sarin
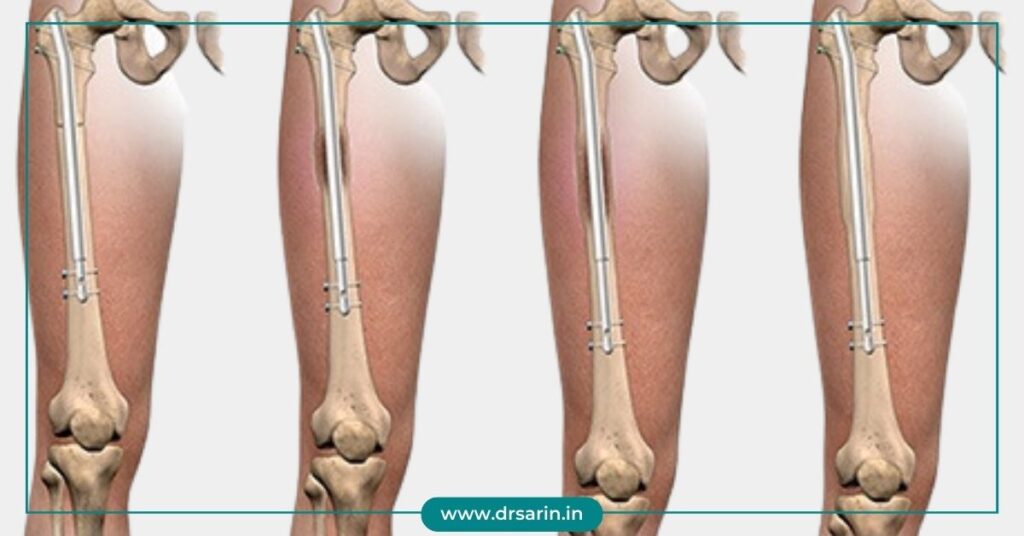
Limb lengthening is a transformative procedure that has evolved significantly over the years, offering new hope and possibilities to those seeking to adjust their stature. Dr. Sarin, a leading expert in orthopedic surgery, has pioneered innovative techniques and approaches in limb lengthening, revolutionizing the field and enhancing patients’ lives. Exploring the Phases of Limb Lengthening Limb lengthening involves a series of carefully orchestrated phases, each crucial in the journey toward achieving the desired increase in height or correcting limb deformities. Dr. Sarin’s approach encompasses these phases to ensure optimal results and patient satisfaction. 1. Pre-Surgical Evaluation Before embarking on the limb-lengthening process, Dr. Sarin conducts a comprehensive assessment. This includes thoroughly examining the patient’s medical history, physical condition, and precise measurements to determine the most suitable approach. 2. Surgical Procedure Under Dr. Sarin’s expertise, the surgical procedure begins with precision and care. Advanced techniques, such as external fixators or internal devices, are employed to make controlled incisions and accurately manage bone adjustments. 3. Lengthening Phase Once the surgical procedure is completed, the lengthening phase commences. This involves gradually separating the bone segments to stimulate new bone growth. Patients work closely with Dr. Sarin and their healthcare team to implement a personalized lengthening schedule, often involving adjustments to the fixators or devices at specific intervals. 4. Consolidation Phase As the desired length is achieved, the consolidation phase begins. This stage focuses on allowing the newly formed bone to solidify and strengthen. Dr. Sarin emphasizes the importance of a tailored rehabilitation program, including physical therapy and regular follow-ups, to facilitate healing. 5. Post-Treatment Care Even after completing the limb lengthening process, Dr. Sarin prioritizes post-treatment care. Follow-up appointments and monitoring ensure the patient’s progress and address potential concerns, promoting long-term success and well-being. Conclusion Dr. Sarin’s dedication to excellence and innovation in limb lengthening surgery has empowered individuals to achieve their desired height goals or correct deformities, enhancing their physical stature and confidence. With a meticulous approach and personalized care throughout the phases, Dr. Sarin has established a legacy of transforming lives through limb lengthening. For those considering limb lengthening, consulting with Dr. Sarin offers a pathway to comprehensive treatment, ensuring a well-informed and supported journey towards achieving their aspirations. Also Read: Bone Healing After Leg Lengthening Surgery Determining Age Limits for Leg Lengthening Surgery External Methods vs. Internal Methods of Cosmetic Leg Lengthening Should Limb Lengthening Surgery be left or Continued? Height Increase Surgery: Purpose, Procedure, and Benefits and Side Effects
