How Safe Is Limb Lengthening Surgery? Risks and Precautions
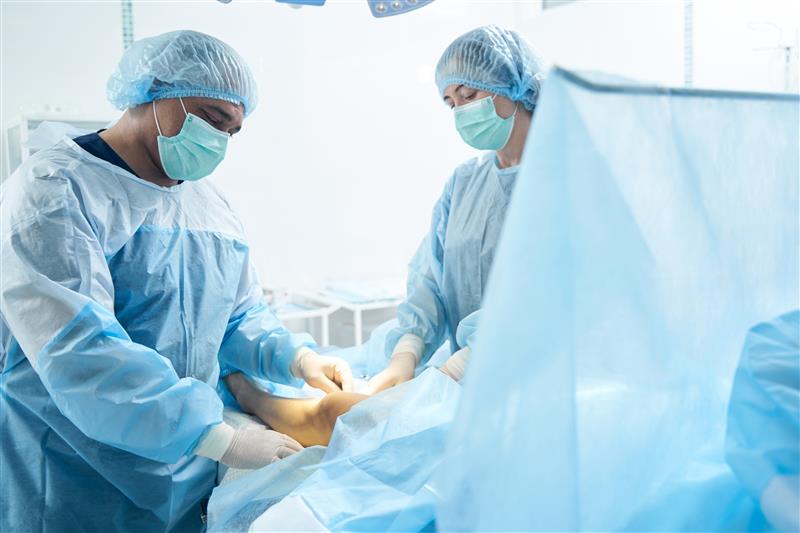
Many people who want to increase their height often ask one simple question: “Is limb lengthening surgery safe?” As a surgeon who performs height increase surgery regularly, I understand why patients are concerned. Any procedure that changes bone structure naturally raises questions about safety, risks, side effects, and cost. Here I’m trying to clear all your doubts about this surgery, I will explain how safe limb lengthening surgery is, the possible risks, and what patients should know before considering height increasing surgery. What Is Limb Lengthening Surgery? Limb lengthening surgery is a medical procedure used to increase a person’s height by gradually lengthening the bones in the legs. Many people also refer to it as: Height increase surgery Bone lengthening surgery Leg lengthening surgery Many patients often ask questions like: Can I increase height by surgery? Is there any surgery to increase height? What is the height increasing surgery name? and the answer of all these queries is: Yes, the procedure exists and is commonly known as limb lengthening surgery. During the surgery, the bone is carefully cut and gradually lengthened using a specialized medical device. Over time, new bone forms in the gap, allowing the leg to grow longer. Most patients can increase their height by 5-8 cm (2-3 inches) through this process. Is Limb Lengthening Surgery Safe? A very common question I hear from patients is: “Is limb lengthening surgery safe or not?” The answer is that limb lengthening surgery can be safe when performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon with proper medical supervision. From my clinical experience, most patients recover well when the surgery is done correctly and when they follow post-surgery physiotherapy and precautions. The Possible Limb Lengthening Surgery Risks Some possible risks of limb lengthening surgery include: Infection: Infections can sometimes occur around the surgical area or fixation device. These are usually treatable with medication if detected early. Nerve Stretching: During the lengthening process, nerves may experience stretching, which can cause temporary numbness or tingling. Joint Stiffness: If physiotherapy is not done regularly, the knee or ankle joint may become stiff. Bone Healing Issues: In rare cases, the new bone may take longer to grow or may need additional support. These are the reasons why patients often ask “how risky is limb lengthening surgery?” Proper surgical planning and monitoring help minimize these risks. Limb Lengthening Surgery Side Effects Some of the side effects of limb lengthening surgery may include: Pain during the lengthening phase Muscle tightness in the legs Temporary swelling Difficulty walking during early recovery In rare cases, leg lengthening complications may occur, but careful follow-up and physiotherapy help manage most issues. Can Height Surgery Go Wrong? Patients sometimes ask: “Can height surgery go wrong?” Complications can happen in any surgical procedure, especially if: The surgery is done by an inexperienced surgeon The patient does not follow rehabilitation instructions The bone is lengthened too quickly That is why choosing the right surgeon and hospital is extremely important for safe limb lengthening surgery. Limb Lengthening Surgery Cost in India The limb lengthening surgery cost in India can vary depending on factors like the surgical technique used, hospital facilities, surgeon expertise, and post-surgery care. Many patients search for height surgery cost or leg lengthening surgery cost in India, but the final cost differs for each patient and treatment plan. Is Limb Lengthening Surgery Safe in India? Another question patients often ask is: “Is limb lengthening surgery safe in India?” Yes, safe limb lengthening in India is possible when the procedure is performed in specialized orthopedic centers with experienced surgeons and proper rehabilitation support. Before choosing a surgeon, patients should always: Research the doctor’s experience Check patient reviews and outcomes Understand the complete treatment plan Who Can Consider Height Increase Surgery? Height increasing surgery is usually suitable for: Adults who want cosmetic height increase Patients with leg length differences Individuals with certain bone conditions Final Words When performed correctly by an experienced surgeon and followed by proper rehabilitation, limb lengthening surgery can be a safe and effective way to increase height. However, it is important to understand the risks of limb lengthening surgery, possible side effects, and the recovery process before making a decision. Consulting a qualified specialist “Dr. Amar Sarin” will help you determine whether height increase surgery is the right option for you. You May Also Like to Know: Average Height Across India 2025 by Select City How Much Height Can You Gain Safely with Limb Lengthening? Indian children may no longer outgrow parents What’s The Average Height Per Country? Psychological Impact Of Limb-Lengthening Surgery
What’s The Average Height Per Country?

Height is one of the most visible traits that vary across populations globally. Multiple factors can influence it, including genetics, environment, nutrition, and healthcare. Countries exhibit different average heights, which can also reflect historical changes in living conditions. Over the years, numerous studies on the average height of individuals in various countries have revealed interesting global trends and differences. Factors Influencing Average Height Before we dive into the numbers, it’s essential to understand the factors influencing average height. The most prominent factors include: Average Height Across Various Countries Let’s explore the average height in different parts of the world: Country Name Average Height (Male) Average Height (Female) India 165 cm 152 cm Netherland 183 cm 170 cm Denmark 181 cm 169 cm United States 175 cm 162 cm Japan 170 cm 158 cm Brazil 173 cm 160 cm China 170 cm 160 cm South Africa 170 cm 158 cm Australia 178 cm 164 cm Germany 180 cm 166 cm 1. Average Height in India India is one of the most populous countries in the world, and average human height in India reflects its diverse genetics and varying access to nutrition. The average height of an adult male in India is approximately 5’5” (5 foot 5 inches) in feet or 165 cm, while the average height of an adult female is 5’0” (5 feet) in Feet or 152 cm. Various studies suggest that while genetics play a role, factors such as malnutrition, socio-economic disparities, and healthcare access contribute to the lower average height compared to Western countries. However, in urban areas where diets are improving, the younger generations are showing slight increases in height. 2. Average Height of People in Netherlands The Dutch are among the tallest people in the world. The average height of an adult male in the netherlands is approximately 6 feet 0r 183 cm, while average netherlands woman height is around 5’7″ (5 feet 7 inches) in feet or 170 cm. Various studies have shown that genetics and a rich, dairy-heavy diet contribute to their taller-than-average stature. 3. Average Height of People in Denmark Like the Netherlands, Denmark also ranks among the countries with the tallest people. The average height for Danish men is about 5’11” (181 cm), and for women, it’s about 5’7″ (169 cm). The high standard of living and access to healthcare and nutritious food are primary contributors to their average height. 4. Average Height of Peoples in United States In the U.S., the average height for men is about 5’9″ (175 cm), while for women, it’s around 5’4″ (162 cm). Although Americans were once among the tallest populations globally, their average height has remained relatively stagnant over the last few decades, possibly due to increased obesity and other lifestyle-related health issues. 5. Average Height of Japanese Japan has a shorter average height compared to Western nations. The average height for Japanese men is about 5’7″ (170 cm), and for women, it’s approximately 5’2″ (158 cm). The traditional Japanese diet, rich in vegetables and fish but low in dairy, has contributed to their shorter stature. However, with changing diets and improved nutrition, younger generations in Japan are showing increases in height. 6. Average Height in Brazil In Brazil, the average height is around 5’8″ (173 cm) for men and 5’3″ (160 cm) for women. Brazil’s ethnic diversity, which includes a mix of European, African, and indigenous ancestry, results in a broad range of heights across the population. 7. Average Height in China In China, the average height for men is around 5’7″ (170 cm), and for women, it’s about 5’3″ (160 cm). Like India, China’s rapid urbanization and economic development have led to improved access to nutrition and healthcare, increasing average height, particularly among the younger population. 8. Average Height of South African Peoples South Africa, known for its diverse population, has an average height of around 5’7″ (170 cm) for men and 5’2″ (158 cm) for women. The population’s mixed ancestry and varying socio-economic conditions contribute to these averages. 9. Average Height of Peoples in Australia In Australia, the average height for men is about 5’10” (178 cm), and for women, it’s around 5’6″ (164 cm). With access to good healthcare, nutritious food, and active lifestyles, Australians rank among the taller populations worldwide. 10. Average Height in Germany Germany is a European country known for its strong economy and high standard of living, and average human height in Germany reflects good nutrition and overall health. The average height of an adult male in Germany is approximately 5’11” (5 foot 11 inches) in feet or 180 cm, while the average height of an adult female is 5’5” (5 foot 5 inches) in feet or 166 cm. Studies indicate that genetics, balanced nutrition, and healthcare access contribute to the relatively taller stature compared to global averages. Urban and younger populations in Germany often show slightly higher heights due to continued improvements in diet and lifestyle. Global Trends in Height Over the past century, the average height in many countries has steadily increased, primarily due to better living conditions and improved nutrition. European countries have seen remarkable increases in average height, while countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America have shown slower growth trends. In developing countries like India, malnutrition and unequal healthcare access are significant factors contributing to shorter stature. However, there are cases where the average height has plateaued or even decreased in specific populations. In the U.S., for instance, the average height has remained relatively stagnant in recent decades, potentially due to the rising rates of obesity and other health issues that affect growth. Final Thoughts The average height of individuals varies widely from country to country and is influenced by many factors, including genetics, nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. While countries like the Netherlands and Denmark boast some of the tallest populations in the world, nations like India, Japan, and China have relatively shorter averages. In India, the average height reflects the country’s socio-economic challenges and disparities in healthcare and nutrition. While
Limb Lengthening Surgery Recovery Time: When Can You Return to Work & Sports?

Limb lengthening surgery recovery time typically ranges between 6-12 months. Most patients return to desk jobs within 8-12 weeks, resume low-impact sports by 3-4 months, and return to high-impact or contact sports between 9-12 months, depending on bone healing, muscle strength, and rehabilitation progress. If you’re wondering whether you can play sports after limb lengthening surgery or how long it takes to fully recover, this detailed guide explains everything step by step. Understanding Limb Lengthening Surgery Recovery Time Recovery after limb lengthening surgery happens in structured phases. Every patient heals at a different speed depending on: Age Amount of length gained Bone healing capacity Pre-surgery fitness level Commitment to physiotherapy 1. Bone Healing Phase (0-3 Months) During the first three months: New bone (regenerate bone) forms gradually You may use crutches or a walker Focus remains on protection and gentle movement This is the most critical phase for bone consolidation. 2. Strength & Mobility Phase (3-6 Months) Once bone formation stabilizes: Muscle strengthening increases Joint flexibility improves Balance and gait training begins Most patients start walking more confidently during this phase. 3. Return to Full Activity (6-12 Months) This stage focuses on: Advanced strengthening Impact tolerance Sports-specific rehabilitation Functional movement training Full recovery timeline varies, but structured rehab ensures safe progress. Leg Lengthening Surgery Recovery Timeline for Sports Here is a simplified sports recovery timeline: Activity Expected Timeline Walking without support 8-12 weeks Swimming 3-4 months Cycling 3-4 months Yoga 3-5 months Light jogging 6-9 months Weight training 6-9 months Football / Basketball 9-12 months This is the typical leg lengthening surgery recovery timeline for return to sports, but clearance from your surgeon is essential. Can You Play Sports After Limb Lengthening Surgery? Yes, most patients can return to sports after limb lengthening surgery. However, the timing depends on: Complete bone healing Muscle strength recovery Joint flexibility Gait normalization Low-impact sports are introduced first, followed by higher-impact activities. Can I Play Football After Limb Lengthening Surgery? Football is a high-impact, contact sport that requires: Strong quadriceps and hamstrings Stable knee and ankle joints Proper balance and coordination Full bone consolidation Most patients can return to football after 9-12 months, once medical clearance is provided and strength testing is satisfactory. Returning too early increases risk of stress fractures or muscle strain. Height Increase Surgery Recovery Time: What to Expect Limb lengthening surgery is often referred to as height increase surgery. The recovery time for height increase surgery generally follows this pattern: 2-3 months for desk job return 4-6 months for moderate physical activity 6-12 months for sports participation Patience and structured physiotherapy are key for safe recovery. Returning to Work After Limb Lengthening Surgery Your return to work depends on your job type: Office-Based Jobs: Most patients return within 8–12 weeks. Physically Demanding Jobs: Jobs requiring standing, lifting, or fieldwork may take 4–6 months. We provide: Medical documentation Gradual work re-entry planning Clearance certificates Step-by-Step Rehabilitation Program Rehabilitation starts within days after surgery. Our structured program includes: Early Stage: Assisted walking with crutches Gentle range-of-motion exercises Pain management strategies Mid Stage: Resistance band exercises Core strengthening Hamstring and calf stretching Advanced Stage: Gait retraining Sport-specific drills Plyometric conditioning This progressive approach reduces long-term stiffness and improves walking symmetry. Preventing Complications During Recovery Without proper rehab, patients may experience: Joint stiffness Muscle tightness Uneven gait Contractures To prevent this: Attend all physiotherapy sessions Avoid running too early Use orthotic support if recommended Do not ignore persistent pain Psychological Support During Recovery Recovery after limb lengthening surgery is both physical and mental. We provide: Emotional counseling Motivation sessions Regular follow-ups Support community access Confidence plays a huge role in returning to sports safely. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): What is the recovery time after limb lengthening surgery? Most patients recover within 6-12 months, depending on activity level and healing speed. Can you play sports after limb lengthening surgery? Yes. Low-impact sports begin around 3-4 months, while contact sports resume after 9-12 months with clearance. Can I run again after leg lengthening surgery? Light jogging usually starts between 6-9 months, depending on bone strength and muscle recovery. Will I regain full strength? With consistent rehabilitation, most patients regain pre-surgery strength. Can I lift weights after height increase surgery? Yes, but progressive loading under supervision is recommended starting around 6 months. Final Thoughts Returning to work and sports after limb lengthening surgery is absolutely possible with the right recovery plan. The key factors are: Patience Structured rehabilitation Regular follow-ups Gradual return to impact activities When recovery is managed correctly, most patients not only return to normal life, but often return stronger and more confident than before. You May Also Like to Read: Limb Lengthening Surgery in 2025 Limb Lengthening Surgery in India How to Lengthen Legs Naturally & Surgically in 2026 Can I Still Run After Height Increase Surgery? Pain Management After Limb Lengthening Surgery
Average Height and Weight chart for Indian Man and Woman

Understanding the average height and weight of men and women can provide insights into a population’s general health and well-being. In India, these averages vary slightly depending on region, diet, and lifestyle. Below is a guide to the average height and weight for Indian men and women, helping you understand where you stand regarding national averages. 1. Average Height and Weight for Indian Men The average Indian male heigh is approximately 5 feet 5 inches to 5 feet 8 inches (165cm to 172 cm), while the average weight ranges between 65-75 kg. However, this can differ based on region, with men from northern states often being taller than those from the other areas due to dietary and environmental factors. Age Group Average Height (cm) Average Weight (kg) 18-25 167-172 60-70 26-35 168-173 65-75 36-45 167-172 68-78 46-60 165-170 70-80 2. Average Height and Weight for Indian Women The average height of an Indian woman is around 5 feet 3 inches (160 cm), while her average weight is typically between 55-65 kg. Like men, women’s height and weight can vary based on nutrition and location. Age Group Average Height (cm) Average Weight (kg) 18-25 152-160 50-60 26-35 154-162 55-65 36-45 153-161 58-68 46-60 151-159 60-70 3. Factors Influencing Indian Average Weight and Height While genetics play a significant role in determining weight and height, other factors such as nutrition, lifestyle, and healthcare access also contribute to variations. For instance, individuals from urban areas often have better access to healthcare and balanced diets, which positively impacts their growth and development. Additionally, regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight. 4. Indian Average Height Trends Indian average height has gradually increased over the years due to improvements in nutrition and healthcare. Younger generations, especially in urban areas, tend to be taller than previous generations. However, despite this growth, Average height remains slightly below global averages. Conclusion Knowing the average height and weight of Indian men and women can help individuals assess their physical health relative to national standards. While genetic factors play a crucial role, lifestyle choices such as a balanced diet and regular exercise are essential in maintaining healthy weight and height proportions. Remember that these averages are just guidelines, and individual health goals should always prioritize overall well-being over societal standards.
Why Ilizarov Technique Is Still the Gold Standard in Complex Cases?

Despite major advancements in orthopaedic surgery, the Ilizarov technique continues to be regarded as the gold standard for treating complex limb conditions. Developed on the principle of controlled bone regeneration, this method has stood the test of time due to its unmatched versatility, reliability, and biological effectiveness. Even today, when modern implants and minimally invasive techniques are available, experienced orthopaedic surgeons continue to rely on the Ilizarov technique for the most challenging cases. Understanding the Ilizarov Technique The Ilizarov technique is based on distraction osteogenesis, a biological process where bone and surrounding tissues regenerate when slowly and precisely stretched. Using a circular external fixator, the surgeon can control bone lengthening, correction of deformities, and healing in multiple planes. What makes this technique unique is that it works with the body’s natural healing ability, rather than replacing it with artificial implants. 1. Unmatched Versatility in Complex Conditions The Ilizarov technique is not limited to a single problem. It is used to treat a wide range of complex orthopaedic conditions, including: Limb length discrepancy Severe angular deformities Non-union and infected non-union of bones Bone loss due to trauma or infection Congenital limb deformities Post-traumatic malalignment No other technique offers the same level of multidirectional correction and adaptability in complex cases. 2. Gold Standard for Infected and Non-Union Cases One of the strongest reasons Ilizarov remains the gold standard is its effectiveness in infected non-union cases. Internal implants often fail in the presence of infection The Ilizarov frame avoids placing foreign material inside infected bone Allows continuous correction while treating infection This makes it the most reliable solution where other surgical methods carry a high risk of failure. 3. Precise and Gradual Deformity Correction Complex deformities often require correction in: Length Angle Rotation Alignment The Ilizarov system allows gradual, millimeter-level adjustments, reducing stress on soft tissues and nerves. This level of precision cannot be safely achieved with one-time corrective surgeries. Gradual correction also lowers the risk of complications such as nerve injury and poor bone healing. 4. Superior Bone Healing Through Natural Regeneration Unlike internal fixation methods that depend on hardware stability, the Ilizarov technique stimulates new bone formation. Key advantages: Strong regenerate bone formation Simultaneous adaptation of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels Reduced risk of bone graft failure This biological advantage is particularly valuable in patients with poor bone quality or previous surgical failures. 5. Effective in Severe Bone Loss and Bone Transport For patients with large bone defects caused by trauma, infection, or tumor removal, the Ilizarov technique enables bone transport. New bone is generated to replace missing segments Limb preservation is possible even in extreme cases Amputation can often be avoided This ability alone makes the Ilizarov method irreplaceable in reconstructive orthopaedics. 6. Suitable for Both Children and Adults The Ilizarov technique can be safely applied across a wide age range. Children benefit from its adaptability during growth Adults benefit from precise correction and strong bone regeneration Because it respects biological healing principles, age is less of a limitation compared to other techniques. 7. Reduced Dependence on Internal Implants In complex cases, internal implants may: Fail due to infection Require multiple revision surgeries Compromise bone biology The Ilizarov technique minimizes reliance on internal hardware, making it safer for patients with previous implant failures or compromised soft tissues. 8. Proven Long-Term Outcomes Decades of global clinical experience have demonstrated: High success rates Durable correction Lower recurrence of deformity Surgeons worldwide continue to rely on the Ilizarov technique because it delivers predictable and lasting results, especially in difficult cases. 9. Surgeon Experience Matters While the Ilizarov technique is powerful, its success depends heavily on the surgeon’s expertise. Complex cases require: Precise planning Deep understanding of bone biology Continuous monitoring and adjustment In experienced hands, the Ilizarov method remains unmatched in treating conditions that other techniques cannot safely address. 10. Why Modern Techniques Haven’t Replaced Ilizarov Modern methods like internal lengthening nails and hybrid techniques have their place, especially in simpler cases. However: They are not suitable for infection They have limited correction capabilities They may not address severe deformities This is why Ilizarov continues to be the first choice in complex and high-risk situations. Conclusion The Ilizarov technique has earned its reputation as the gold standard in complex orthopaedic cases due to its: Versatility Biological approach to healing Precision in correction Effectiveness in infection and non-union Ability to preserve limbs in severe cases Even with modern surgical advancements, no other technique offers the same reliability in challenging conditions. When complexity increases, the Ilizarov method remains the most trusted solution in reconstructive orthopaedics. For patients facing complicated limb problems, choosing an experienced surgeon who masters the Ilizarov technique can make a life-changing difference. Also Read: Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Limb Lengthening Surgery? Genetic Influences on Height What is Dwarfism? Average Height For A Man In India 2026 Average Height Across India 2026 by Select City
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Limb Lengthening Surgery?

Limb lengthening surgery is a highly specialized orthopaedic procedure designed to increase bone length, correct deformities, or address limb length discrepancies. While the surgery has advanced significantly over the years, it is not suitable for everyone. Identifying the right candidate is crucial for safe outcomes, effective healing, and long-term success. This blog explains who is an ideal candidate for limb lengthening surgery, based on medical criteria, physical readiness, and realistic expectations. Understanding Limb Lengthening Surgery Limb lengthening surgery works on the principle of distraction osteogenesis, where bone is carefully cut and gradually stretched, allowing new bone to regenerate in the gap. Techniques such as Ilizarov, LON (Lengthening Over Nail), and other modern methods are used depending on the patient’s condition. Because the procedure involves bone regeneration, soft tissue adaptation, and long rehabilitation, candidate selection is critical. 1. Patients with Limb Length Discrepancy One of the most common and medically justified reasons for limb lengthening surgery is limb length discrepancy (LLD). Ideal candidates include: Patients with one leg or arm shorter than the other Discrepancy caused by birth defects, injury, infection, or previous surgery Functional issues such as limping, back pain, or posture imbalance When non-surgical methods like shoe lifts are insufficient, limb lengthening offers a permanent correction. 2. Individuals with Congenital Bone Deformities Patients born with congenital bone conditions are strong candidates for limb lengthening surgery. This includes: Congenital short bones Angular deformities Developmental limb abnormalities In such cases, limb lengthening not only improves length but also restores alignment and function, helping patients lead a more normal and active life. 3. Patients with Short Stature or Dwarfism Limb lengthening surgery can be an option for individuals with dwarfism or medically diagnosed short stature, especially when height significantly impacts mobility, independence, or quality of life. Ideal candidates: Have completed most of their natural growth Are medically stable Understand the physical and emotional demands of the process The surgery is often done in stages and requires careful planning and long-term follow-up. 4. Adults Seeking Height Increase Surgery (With Realistic Expectations) Some adults consider limb lengthening surgery for height increase, but only those who meet strict medical and psychological criteria are considered suitable. An ideal candidate must: Be physically healthy with good bone quality Have realistic expectations about achievable height gain Be willing to commit to rehabilitation and follow medical advice Height increase surgery is not a cosmetic shortcut-it is a complex orthopaedic procedure requiring discipline and patience. 5. Patients with Bone Non-Union or Post-Traumatic Conditions Limb lengthening surgery is often used in complex trauma cases where: Bones fail to heal properly (non-union) Significant bone loss has occurred due to injury or infection Through bone transport and lengthening techniques, limb length and strength can be restored while preserving the natural limb. 6. Age Considerations: Who Falls in the Safe Range? Age plays an important role in determining candidacy. Generally suitable age groups: Late adolescents (after growth plate closure) Adults up to middle age with good bone health Older patients may still be eligible if they: Have good overall health Do not suffer from severe osteoporosis or chronic illnesses Chronological age matters less than bone quality and healing capacity. 7. Good Physical Health Is Essential An ideal candidate must be medically fit. Patients should: Have no uncontrolled diabetes, severe heart disease, or immune disorders Be free from active infections Have good nutritional status Strong muscles, healthy skin, and adequate blood circulation support better recovery and reduce complications. 8. Psychological Readiness and Mental Strength Limb lengthening surgery is a long journey that requires mental resilience. Ideal candidates: Understand the length of treatment and recovery Are emotionally stable and patient Can manage temporary discomfort and lifestyle changes Patients with unrealistic expectations or poor compliance are not ideal candidates, regardless of physical eligibility. 9. Willingness to Commit to Rehabilitation Rehabilitation is as important as the surgery itself. Ideal candidates: Are committed to daily physiotherapy Follow post-operative instructions strictly Attend regular follow-up appointments Without proper rehabilitation, even technically successful surgery may not deliver optimal results. 10. Who Is NOT an Ideal Candidate? Limb lengthening surgery may not be recommended for individuals who: Have severe osteoporosis Suffer from uncontrolled chronic illnesses Are unable to commit to rehabilitation Have unrealistic expectations about outcomes Seek instant results without understanding the process A thorough evaluation helps avoid unnecessary risks. How Candidacy Is Determined Before recommending limb lengthening surgery, specialists conduct: Detailed physical examination Imaging studies (X-rays, scans) Assessment of bone quality and alignment Psychological evaluation Discussion of goals and expectations This ensures that surgery is both safe and beneficial for the patient. Conclusion An ideal candidate for limb lengthening surgery is someone who: Has a genuine medical or functional need Is physically healthy with good bone quality Is mentally prepared for a long recovery Has realistic expectations Is committed to rehabilitation and follow-up care When performed on the right candidate by an experienced orthopaedic surgeon, limb lengthening surgery can significantly improve mobility, symmetry, confidence, and quality of life. Also Read: Genetic Influences on Height What is Dwarfism? Average Height For A Man In India 2026 Average Height Across India 2026 by Select City What is Limb Discrepancy?
Genetic Influences on Height: Exploring 7 Factors Affecting Human Height Stature

Height has long been a topic of fascination and curiosity. People often wonder why some individuals tower over others while others remain petite. The debate surrounding whether height is predominantly governed by genetics or influenced by various other factors is ongoing. Let’s delve into the intricate web of influences on human height and explore the seven key factors affecting human height growth and play pivotal roles in determining this aspect of our physicality. 1. DNA: The Blueprint of Stature At the heart of the height puzzle lies our DNA. Our genetic makeup acts as the initial map, laying the groundwork for our potential height. Research indicates that 60–80% of a person’s height potential is inherited from their parents. Variations in specific genes, including those related to growth hormone production and bone development, contribute significantly to how tall or short a person may become. Height is a polygenic trait, meaning it is influenced by multiple genes rather than a single “height gene.” How do height genetics work? Genes regulate bone growth, growth plate activity, and hormone production Both parents contribute equally to a child’s height potential Boys often inherit height patterns influenced by both maternal and paternal genetic lines Here it is notable, genetics only defines the maximum potential height, it does not guarantee the final outcome. 2. Hormones: The Growth Orchestrators Hormones act as messengers within the body, orchestrating growth and development. Growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, plays a fundamental role in stimulating growth and regulating height. Additionally, sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone also impact human growth patterns, with males and females experiencing growth spurts at different stages of adolescence. Hormonal imbalances during childhood or adolescence can significantly affect height growth. Key hormones involved: Growth Hormone (GH): Stimulates bone and tissue growth Thyroid Hormones: Regulate metabolism and skeletal development Sex Hormones (Estrogen & Testosterone): Trigger adolescent growth spurts and growth plate closure 3. Nutrition: The Building Blocks of Growth Nutrition forms the cornerstone of physical development, including height. A balanced diet that includes essential nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, minerals (mainly calcium and vitamin D), and adequate calories is crucial for optimal human height growth. Malnutrition, particularly during critical growth periods, can stunt growth potential, leading to shorter stature. Nutrients critical for huam height growth: Protein (for tissue building) Calcium & Vitamin D (for bone strength) Zinc & Magnesium (for growth regulation) Adequate calories during growth years 4. Environment: The External Influence Beyond genetics and nutrition, the environment we grow up in significantly influences our height. Factors like access to quality healthcare, pollution exposure, and socioeconomic conditions can impact growth. Adverse environmental conditions, such as toxins or inadequate healthcare exposure, can hinder proper growth and contribute to shorter stature. 5. Living Conditions: The Comforts and Constraints The quality of living conditions, including access to clean water, sanitation, and healthcare facilities, is vital in determining a person’s height. Socioeconomic disparities can limit access to these essentials, affecting overall health and influencing an individual’s ultimate height potential. Children raised in healthier environments generally achieve greater height compared to those with poor living conditions. 6. Gender: Nature’s Distinction Nature has designed males and females differently, and this distinction extends to growth patterns. On average, males tend to be taller than females due to hormonal differences and genetic predispositions. However, variations within genders are vast, highlighting the multifaceted nature of height determination. Biological differences explain average height variations between genders. Gender plays a natural role in height differences: On average, men are taller than women Boys experience later but longer growth spurts Girls mature earlier and stop growing sooner due to earlier growth plate closure 7. Physical Activity: Striving Toward Verticality While genetics set the stage and nutrition fuels growth, physical activity is a catalyst. Regular exercise and physical activity, especially during childhood and adolescence, promote bone health, stimulate growth, and contribute to overall stature. Engaging in activities that encourage stretching and weight-bearing exercises can positively impact height potential. In other words we can say, Physical activity supports bone density, posture, and muscle development, especially during growth years. Can exercise increase height? In children & adolescents: Exercise supports optimal growth In adults: Exercise does NOT increase bone length Can sprinting increase height? No. Sprinting improves muscle strength and posture but cannot increase height after growth plates close. Age & Growth Plate Closure Height growth depends on open epiphyseal (growth) plates. Age Group Height Increase Possible? Childhood ✅ Yes Adolescence ✅ Yes After puberty (18–21+) ❌ No (naturally) Can Height Be Increased After Growth Stops? Natural Method: After adulthood nutrition, exercise, stretching, Posture correction may help you to look a little taller by improving your posture. But, do not increase actual height. Limb Lengthening Surgery: A Medical Height Increase Option For adults who wish to increase height, limb lengthening surgery is the only scientifically proven method to permanently increase height after growth completion. From an orthopaedic standpoint: Height is biologically limited after skeletal maturity Claims of adult height increase through exercises or supplements are not medically supported Surgical options should be considered only after proper evaluation A qualified limb lengthening specialist evaluates: Bone health Psychological readiness Functional expectations Long-term outcomes Conclusion In conclusion, while genetics form the backbone of height determination, many factors intricately weave together to shape an individual’s ultimate stature. Understanding these influences can show how to optimize growth potential and underscore the importance of holistic well-being in achieving one’s maximum height. As we navigate the complex interplay between genetics, environment, nutrition, and lifestyle factors, it becomes evident that height is not solely a result of genetic inheritance but a harmonious symphony of various influences that sculpt our physical selves. Frequently Asked Questions (SEO-Optimized) Q1. What factors affect height growth? Genetics, hormones, nutrition, environment, physical activity, gender, and overall health. Q2. Where does height come from? Height comes primarily from inherited genes, influenced by nutrition, hormones, and growth conditions. Q3. Who do you get your height from? Both parents contribute equally to height genetics. Q4. What makes you tall?
What is Dwarfism? | Top Causes, Symptoms & Modern Treatments

What is Dwarfism? It’s a medical condition characterized by short stature resulting from genetic, hormonal, or bone development disorders. In most cases, adults with dwarfism reach a height of 4 feet 10 inches (147 cm) or below, though this can vary. Dwarfism affects bone growth, limb proportions, and sometimes overall physical function. With proper diagnosis and modern treatment options-including orthopedic care-individuals with dwarfism can lead full, active, and empowered lives. Understanding Dwarfism Definition of Dwarfism Dwarfism refers to abnormally short stature caused by genetic or medical conditions that affect bone and cartilage development. It may involve shortened limbs, abnormal proportions, or slow growth rates. More than 200 medical conditions can cause dwarfism, making accurate evaluation essential. Medical Criteria for Diagnosis Doctors typically diagnose dwarfism when: A child’s height is significantly below average for age Growth velocity is slower than expected Limb proportions appear different Genetic markers indicate a growth disorder Types of Dwarfism Disproportionate Dwarfism This is the most common type. Characteristics include: Normal-sized torso Shortened limbs Curved spine Bow legs or knock knees Larger head with prominent forehead Examples: Achondroplasia Diastrophic dysplasia Proportionate Dwarfism In this form, the body is small but well-proportioned. It is often linked to: Growth hormone deficiency Genetic syndromes Metabolic or endocrine disorders Causes of Dwarfism Genetic Causes Around 80% of achondroplasia cases occur due to a spontaneous genetic mutation. If one parent has dwarfism, there is a 50% chance of passing it to the child. Hormonal & Growth Disorders These include: Growth hormone deficiency Hypothyroidism Pituitary gland disorders Such conditions affect the body’s ability to produce growth-regulating hormones. Congenital Bone Disorders Some individuals develop dwarfism due to: Skeletal dysplasia Cartilage abnormalities Poor bone mineralization These issues alter normal bone structure and growth. Signs & Symptoms of Dwarfism Symptoms vary widely, but common signs include: Short arms and legs Delayed growth (childhood) Limited joint movement Bow legs Curved spine (kyphosis or lordosis) Larger-than-average head size Frequent ear infections (in some types) How Dwarfism Affects Daily Life? Dwarfism may influence: Mobility and walking style Ability to reach household items Joint stress and fatigue Social challenges or confidence issues However, with the right support and treatment, individuals lead completely independent lives. Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Dwarfism? Physical Examination Doctors assess: Growth patterns Limb proportions Spinal alignment Joint flexibility Imaging and Genetic Tests To determine the exact type, specialists use: X-rays MRI or CT scans Genetic analysis Hormone level testing Treatment Options for Dwarfism Growth Hormone Treatments Used primarily for proportionate dwarfism, these help increase growth velocity in childhood. Orthopedic Interventions Includes correction of: Bow legs Knock knees Spinal curvature Joint problems These treatments improve mobility and prevent long-term discomfort. Limb Lengthening for Dwarfism Modern orthopedic methods allow gradual and safe height improvement. Techniques include: Ilizarov External Fixators LON (Lengthening Over Nail) PRECICE magnetic nails These advanced methods help increase height, balance limb proportions, and enhance overall quality of life. Dwarfism Treatment by Dr. Amar Sarin Dr. Amar Sarin is one of Asia’s most experienced Limb Lengthening and Dwarfism correction specialists, with over 30 years of expertise and more than 3000 successful Ilizarov and reconstructive surgeries. Trained at Russia’s renowned Center for Reconstruction and Regeneration Surgeries, he combines world-class orthopedic techniques with compassionate care. Patients trust Dr. Sarin for safe, precise, and life-enhancing solutions tailored to their unique needs. Living with Dwarfism: Mobility & Adaptations People with dwarfism may benefit from: Customized furniture Modified vehicles Simple home adjustments Physiotherapy Occupational therapy These improve independence and daily comfort. Risks, Challenges & Long-Term Health Considerations Individuals may face: Chronic joint pain Early arthritis Spinal problems Ear infections (in certain types) Breathing issues (rare) With regular monitoring, these complications can be managed effectively. When to Seek Specialist Care Consult an orthopedic or genetic specialist if: Growth seems slower than average Child has abnormal limb proportions There is family history of dwarfism Mobility issues affect daily life Height-related concerns require evaluation Early diagnosis ensures the best treatment outcomes. FAQs About Dwarfism Q1. Is dwarfism always genetic? Ans: Not always. While many cases are genetic, some result from hormonal or bone-growth disorders. Q2. Can dwarfism be cured? Ans: Dwarfism itself cannot be “cured,” but symptoms and height differences can be managed with proper treatment. Q3. What age is ideal for limb lengthening in dwarfism? Ans: Older children, teens, and adults can undergo limb lengthening. The timing depends on growth stage and medical evaluation. Q4. Does dwarfism affect intelligence? Ans: No, dwarfism does not affect cognitive ability. Q5. Can people with dwarfism live a normal life? Ans: Absolutely. With proper care, mobility support, and orthopedic treatment, individuals live full, active lives. Conclusion Dwarfism is a diverse medical condition that affects bone growth, stature, and body proportions. With today’s advancements in genetic evaluation, orthopedic treatment, and limb lengthening technologies, individuals with dwarfism can overcome physical challenges and enjoy higher levels of comfort, mobility, and confidence. Guided by experienced specialists like Dr. Amar Sarin, patients receive personalized care designed to enhance their health and overall quality of life. You May Also Like: What is Limb Discrepancy? Cross-Leg Lengthening Surgery in India Femur vs Tibia Lengthening Shoe Lifts for Height Precice Cost in India | Limb Lengthening
Average Height For A Man In India 2026

In 2026, the average height of men in India showcases a wide variety shaped by numerous influences. Exploring the elements that contribute to the average height in India offers important perspectives on the trends of physical growth and development among the Indian populace. Indian Average Height: Indian Chart Average height in India varies across regions, ethnicities, socioeconomic backgrounds, and other demographic factors. While there is no singular “Indian Average Height,” studies have reported that the average height for a man ranges from approximately 5 feet 3 inches to 5 feet 6 inches for adult males and 4 feet 9 inches to 5 feet 2 inches for adult females. These averages may vary based on the population studied and the methodology used to collect height data. Factors Affecting India’s Average Height Several factors contribute to the variation in average height in India observed among individuals: 1. Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual’s height. Variations in genetic traits inherited from parents can influence height potential, with specific populations exhibiting taller or shorter average heights due to genetic predispositions. 2. Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is crucial for optimal growth and development during childhood and adolescence. Malnutrition, micronutrient deficiencies, and poor dietary practices can stunt growth and lead to shorter stature in adulthood. Access to nutritious food, especially during critical periods of growth, significantly impacts average height within populations. 3. Healthcare: Access to healthcare services, including prenatal care, pediatric care, and disease prevention programs, can influence growth trajectories and overall health outcomes. Improved healthcare infrastructure and healthcare-seeking behavior contribute to better health and nutrition outcomes, potentially leading to taller average heights for a man in specific regions or populations. 4. Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic status, including income, education, and living conditions, can affect access to resources essential for healthy growth and development. Individuals from higher socioeconomic backgrounds may have better access to nutritious food, healthcare services, and environmental conditions conducive to growth, contributing to taller average heights within those populations. 5. Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as pollution, climate, and urbanization can impact health and well-being, potentially influencing growth patterns and average female height. Urban areas may experience different growth trends compared to rural areas, reflecting variations in lifestyle, diet, and exposure to environmental stressors. 6. Ethnic Diversity: India is characterized by significant ethnic and cultural diversity, with distinct populations exhibiting unique genetic traits and growth patterns. Ethnic differences in average height may reflect genetic variations, historical influences, and cultural practices specific to each group. The average height for a man of individuals in India in 2026 reflects a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, socioeconomic, and healthcare factors. While no single “Average Height In India” exists, understanding the diverse factors shaping physical growth and development provides valuable insights into population health and well-being. Efforts to address nutrition, healthcare access, socioeconomic disparities, and environmental challenges are essential for promoting optimal growth and achieving healthier height outcomes across the Indian population. Also Read: Are there any height increase pills to foster height growth? Lengthening In Four Segments The Science Behind Height Lengthening Preparing for a Successful Limb Lengthening Surgery and a Healthy Recovery Doctor says leg-lengthening surgery is increasingly popular among men who wish to be taller
Average Height Across India 2026 by Select City

Height serves as an important measure of overall health, nutrition, and well-being, with variations seen across different cities and regions in India. This article delves into the average height in various Indian cities for 2026, examining the trends and factors that contribute to these disparities. The information gathered offers valuable perspectives on lifestyle, genetics, and nutritional habits in India. Average Height in India: National Overview On a national level, the average height in India has shown gradual increases over the past decades. While genetics play a significant role in determining height, socioeconomic factors, access to healthcare, and dietary habits also have substantial impacts. As of 2026, the average height for males and females in India is approximately: Men: 5 feet 5 inches (165 cm) Women: 5 feet (152 cm) However, these figures can fluctuate widely depending on specific urban and rural settings. Factors Influencing Height Variation in India Height is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In India, socioeconomic status, dietary diversity, and healthcare access all contribute significantly to height variations. Key influences include: City-Wise Analysis of Average Heights in India (2026) 1. New Delhi In the capital city, a diverse population and relatively high standard of living contribute to a higher-than-average height. However, factors like pollution may hinder optimal growth. In 2024, average heights are: Men: 5 feet 6 inches (168 cm) Women: 5 feet 1 inch (155 cm) 2. Mumbai Mumbai, known for its bustling urban life, has a mixed demographic, with people from various socioeconomic backgrounds. Access to nutritious food is more widespread, though stress and pollution remain concerns. Men: 5 feet 5 inches (165 cm) Women: 5 feet (152 cm) 3. Chennai Chennai’s population sees slightly lower average heights, partly due to dietary habits and regional genetics. The tropical climate and diet rich in rice and less protein might impact height trends. Men: 5 feet 4 inches (163 cm) Women: 4 feet 11 inches (150 cm) 4. Kolkata With a strong cultural emphasis on a carb-heavy diet, the population in Kolkata tends to have shorter average heights. The city’s lifestyle, dietary habits, and genetics contribute to this trend. Men: 5 feet 4.5 inches (164 cm) Women: 4 feet 11 inches (150 cm) 5. Bengaluru Known for its tech industry and youthful demographic, Bengaluru’s average height is slightly higher due to access to varied diets and healthcare. Men: 5 feet 5.5 inches (166 cm) Women: 5 feet (152 cm) 6. Ahmedabad Ahmedabad shows moderate height averages. While the diet is generally nutritious, it is high in carbohydrates and fats, which may influence growth. Men: 5 feet 5 inches (165 cm) Women: 5 feet (152 cm) Rural vs. Urban Height Trends There’s a clear distinction in average height between urban and rural areas. Urban residents tend to be taller due to better healthcare facilities and balanced diets. Conversely, rural areas, especially those with limited access to nutritious food, report lower averages. Bridging this gap remains essential for enhancing health equity. How Socioeconomic Conditions Affect Average Heights Socioeconomic conditions are one of the biggest factors influencing height. Areas with higher income levels and better infrastructure offer more resources for health and well-being. In cities, access to fortified foods, regular medical check-ups, and adequate housing contribute to better growth outcomes in children and adolescents. Comparison with Global Averages When compared internationally, India’s average height is still below the global average. Countries with advanced healthcare systems and higher protein intake generally have taller populations. Analyzing these differences highlights the importance of healthcare and nutritional investments in raising the national average. Conclusion While genetics set a base, lifestyle, nutrition, and healthcare largely determine the actual growth of individuals across different regions. India can work towards a higher average height by increasing awareness of balanced diets and improving healthcare access, especially in rural and low-income urban areas. The study of Indian average height by city sheds light on how public health initiatives can continue to improve nationwide. You May Also Like to Know: How Much Height Can You Gain Safely with Limb Lengthening? Indian children may no longer outgrow parents What’s The Average Height Per Country? Psychological Impact Of Limb-Lengthening Surgery Hip Replacement Surgery
