
What’s The Average Height Per Country?
Height is one of the most visible traits that vary across populations globally. Multiple factors can influence it, including genetics, environment, nutrition, and healthcare. Countries

Height is one of the most visible traits that vary across populations globally. Multiple factors can influence it, including genetics, environment, nutrition, and healthcare. Countries

Limb lengthening surgery recovery time typically ranges between 6-12 months. Most patients return to desk jobs within 8-12 weeks, resume low-impact sports by 3-4 months,

Understanding the average height and weight of men and women can provide insights into a population’s general health and well-being. In India, these averages vary

Despite major advancements in orthopaedic surgery, the Ilizarov technique continues to be regarded as the gold standard for treating complex limb conditions. Developed on the

Limb lengthening surgery is a highly specialized orthopaedic procedure designed to increase bone length, correct deformities, or address limb length discrepancies. While the surgery has

Height has long been a topic of fascination and curiosity. People often wonder why some individuals tower over others while others remain petite. The debate

What is Dwarfism? It’s a medical condition characterized by short stature resulting from genetic, hormonal, or bone development disorders. In most cases, adults with dwarfism

In 2026, the average height of men in India showcases a wide variety shaped by numerous influences. Exploring the elements that contribute to the average

Height serves as an important measure of overall health, nutrition, and well-being, with variations seen across different cities and regions in India. This article delves

What is Limb Discrepancy?: It’s a condition where one leg or arm is shorter than the other. This difference may be mild and barely noticeable,
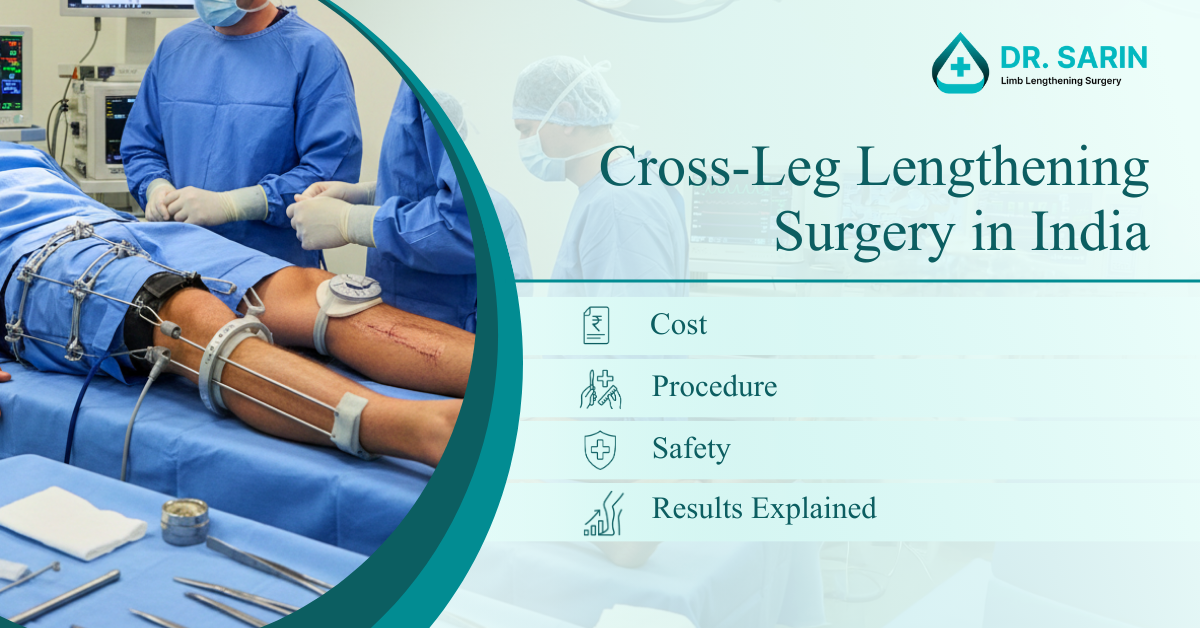
Limb lengthening surgery has evolved significantly over the last two decades. One of the most advanced and reliable methods used today in India is the

Height increase surgery has become one of the most advanced and life-changing procedures in modern orthopaedics. But one of the most common questions patients ask

Height is something many people wish they had more of. Whether for confidence, social reasons, or professional presence, appearing taller can make a difference. One

Most teens are wondering: Can you become taller after the age of 18? Although natural growth will stop or slow down after adolescence, nutrition, posture,

Average Height in USA: Gaining insight into the average height of populations can reveal important information about health, nutrition, and genetics. Let’s explore the USA

For many people, increasing their height or correcting a limb length difference is a life-changing decision. With modern technology, this is now possible through advanced
In today’s fast-paced world, physical appearance plays a significant role in confidence and self-esteem. This surgery has emerged as a viable option for those seeking

Limb lengthening surgery has gained popularity in recent years as a medical procedure that offers individuals the opportunity to enhance their height. While the desire

Surgeons often use an external fixator for limb lengthening procedures due to its effectiveness in gradually and precisely lengthening bones. This device consists of external

Considering leg-lengthening surgery is a significant decision that can have a transformative impact on your life. Dr. Sarin, a distinguished figure in orthopedic surgery, offers

Bone lengthening, such as the innovative procedures offered by Dr. Sarin, can be a life-changing solution for individuals seeking to increase their height or address

It is a groundbreaking procedure that can significantly improve the lives of individuals seeking to address limb length discrepancies or achieve their desired height. However,

Leg lengthening surgery, a medical procedure designed to increase a person’s height, is a complex and intricate process that involves the elongation of bones in

In recent years, an intriguing trend has emerged in cosmetic procedures: leg-lengthening surgery. This groundbreaking procedure, offered by esteemed professionals like Dr. Sarin, has piqued

Limb lengthening surgery is a medical procedure that has gained attention for its potential to enhance the stature of individuals who desire it. Dr. Sarin,

The history of limb lengthening is a fascinating journey through medical innovation, perseverance, and the quest for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with

Leg lengthening surgery, a medical procedure that can increase an individual’s height, has become increasingly popular for those seeking to enhance their physical appearance or

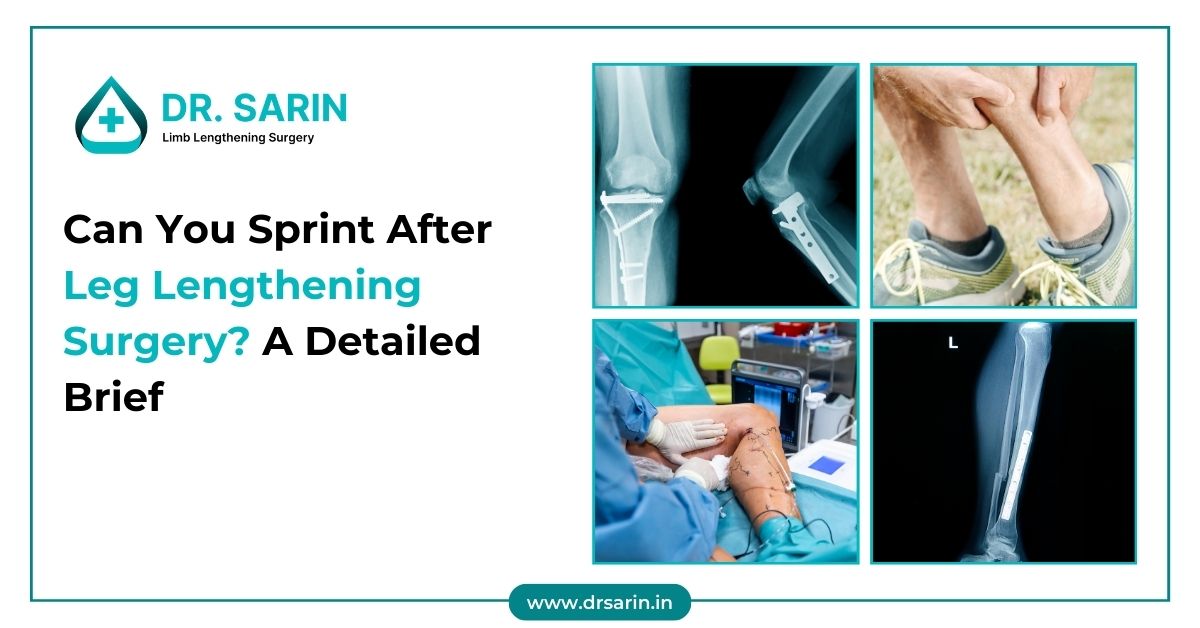
Limb lengthening surgery is a life-changing procedure that often raises questions about physical activity and sports participation during and after recovery. In this article, we’ll

Limb lengthening is a transformative procedure that has evolved significantly over the years, offering new hope and possibilities to those seeking to adjust their stature.

If you’ve ever dreamt of gaining a few extra inches in height, Height Surgery could be the transformative solution you’ve been seeking. This comprehensive guide

In a world where confidence and self-assuredness are highly valued, height can play a significant role in one’s self-esteem. For those who have long wished

Cosmetic leg lengthening, also known as limb lengthening, is a surgical procedure designed to increase a person’s height for aesthetic purposes. It’s a choice made

In recent years, limb-lengthening surgery has gained attention for its potential to transform lives by addressing height-related insecurities and medical conditions. Yet, there is often
Quadrilateral lengthening is a groundbreaking medical procedure that’s transforming lives and restoring mobility for individuals with specific orthopedic conditions. Dr. Sarin, a pioneer in this

Limb lengthening surgery is a transformative procedure that requires careful consideration during the recovery period and in the postoperative phase. Appropriate exercise and physical activities

Limb lengthening surgery is a medical procedure that has gained attention for its potential to address height-related concerns. However, amidst the curiosity, several myths surround

Limb lengthening surgery is a remarkable procedure that offers the possibility of increasing height or correcting limb deformities. However, the success of this surgery doesn’t

Undergoing leg lengthening surgery marks the beginning of a transformative journey towards improved mobility and quality of life. The initial 10 days following the procedure

In recent years, there has been a notable shift in attitudes towards cosmetic procedures among men. Traditionally considered a taboo topic, the realm of male

Returning to work and resuming daily life after limb-lengthening surgery can be gradual but rewarding. This transformative procedure, often pursued by individuals seeking to address

Understanding the average heights of men and women globally provides insights into various health, nutrition, and socio-economic factors. Examining these averages across different regions and

Short stature, often a source of concern for individuals and parents, can be attributed to various factors. Understanding the causes, diagnostic procedures, and available treatment
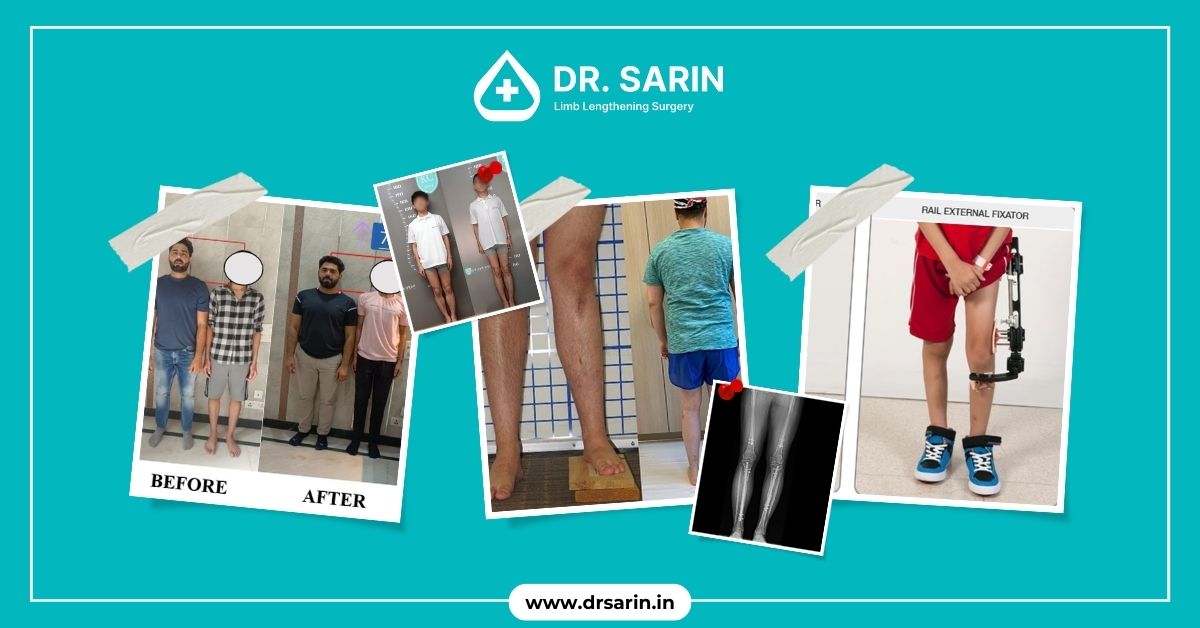
Many individuals wonder if it’s possible to increase height after puberty, and the answer is yes. While the growth plates close after puberty, there are

Limb lengthening surgery, a revolutionary medical procedure, aims to increase the length of limbs for various reasons, such as correction of deformities, enhancing stature, or
Leg lengthening surgery is a transformative procedure that offers individuals the chance to enhance their stature and correct limb length discrepancies. However, the post-surgery phase

Limb lengthening surgery, a procedure often utilized to correct limb length discrepancies or address congenital conditions, can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.

Launching on the journey of leg lengthening surgery is not merely a physical transformation; it’s a profound psychological experience encompassing anticipation, decision-making dilemmas, expectations, and

Deciding to undergo limb-lengthening surgery is a significant step towards achieving desired height or correcting limb length discrepancies. However, selecting the ideal approach between femur

Lengthening procedures are intricate orthopedic surgeries designed to address limb length discrepancies and deformities, enhancing function and improving the quality of life for patients. This
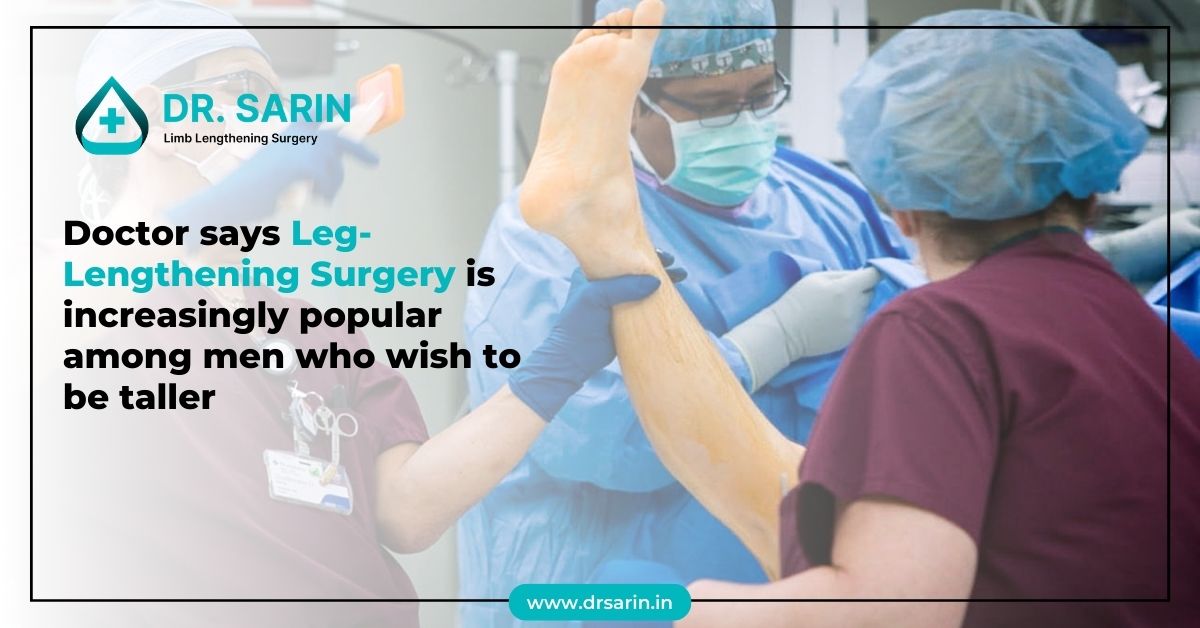
Leg-lengthening surgery, once primarily associated with medical necessity, is now gaining popularity among men who desire to increase their height for cosmetic reasons. This trend

Height is primarily determined by genetics and influenced by various factors such as nutrition, environment, and hormonal balance. While no drugs are specifically designed to

Limb lengthening is a surgical procedure designed to correct discrepancies in limb length, congenital deformities, or injuries. This advanced orthopedic technique involves cutting and gradually

Limb lengthening surgery is a significant medical procedure that requires careful preparation and planning for a successful outcome and smooth recovery. Whether you’re considering limb

It is a complex orthopaedic procedure aimed at correcting limb length discrepancies or deformities. This innovative surgical technique involves gradually elongating bones using external or

The question, can height be increased after 21 is common, especially for individuals who may be dissatisfied with their current stature. While height increase is

Leg lengthening and arm lengthening are both complex medical procedures aimed at increasing the length of limbs. However, they differ significantly in terms of techniques,
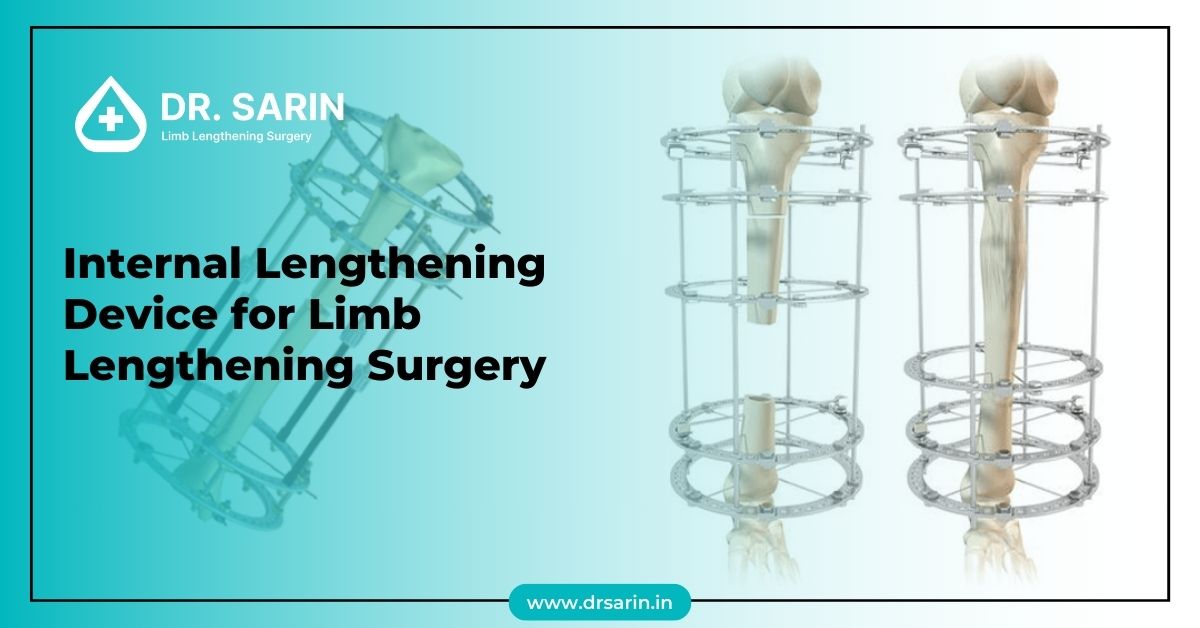
Limb lengthening surgery using an internal lengthening device is a sophisticated procedure designed to address various orthopedic conditions and improve the quality of life for
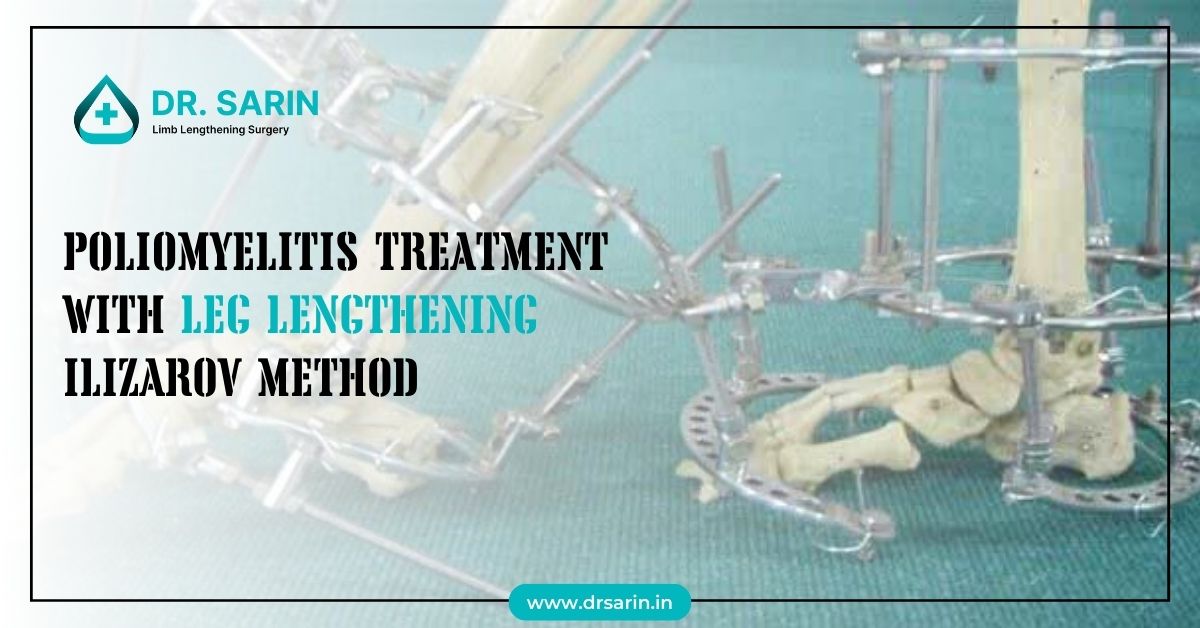
Poliomyelitis, commonly known as polio, can lead to muscle weakness and paralysis. It often affects the legs and results in limb length discrepancies. The Ilizarov

Height lengthening, once thought to be solely determined by genetics, is now possible through advancements in medical science. Understanding the intricate processes involved sheds light
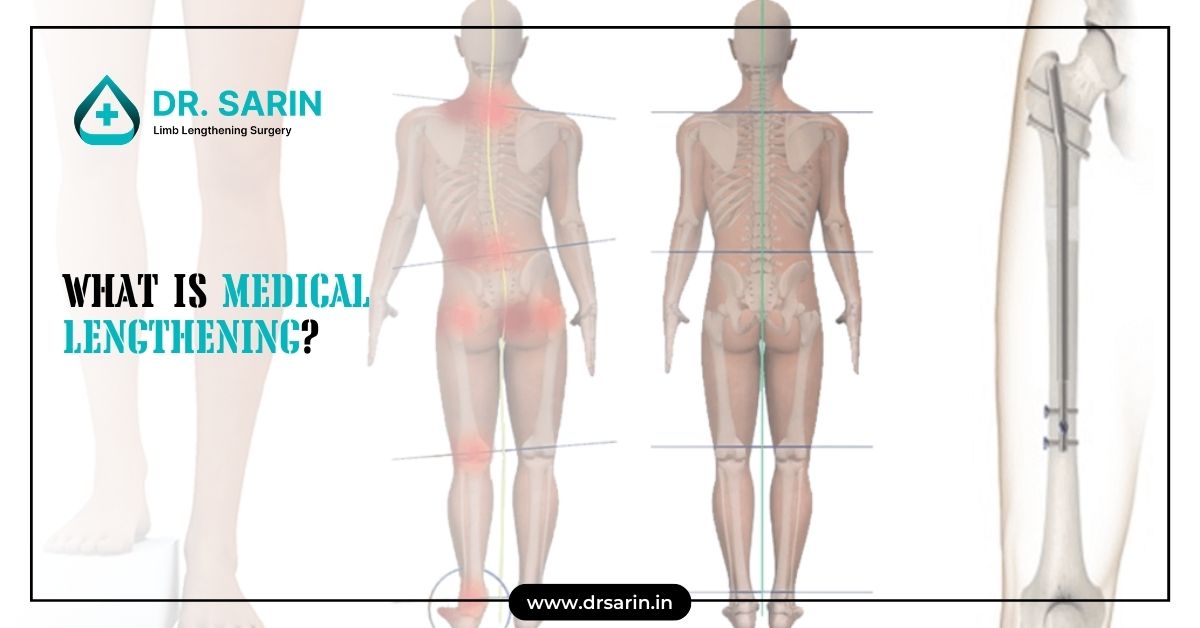
What is Medical Lengthening? Medical lengthening, often referred to as limb lengthening, is a surgical procedure aimed at increasing the length of bones in the

Height is often seen as a genetic trait that primarily influences physical appearance but can also significantly affect overall health. From cardiovascular health to mental
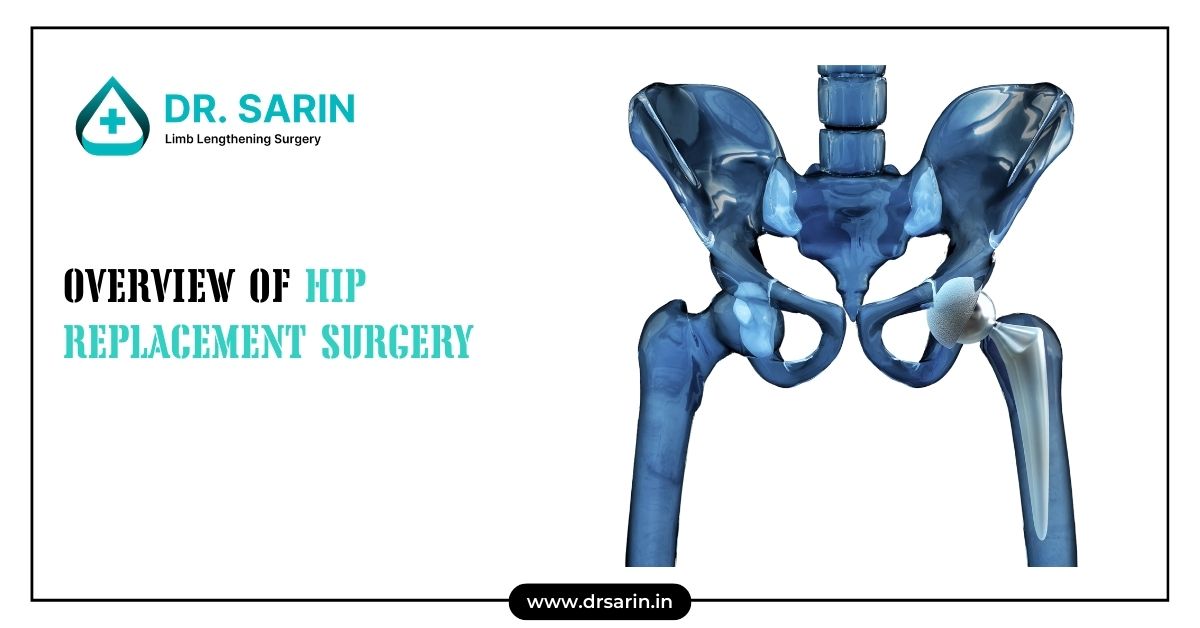
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a common procedure aimed at relieving hip pain and improving joint function. This surgery involves removing
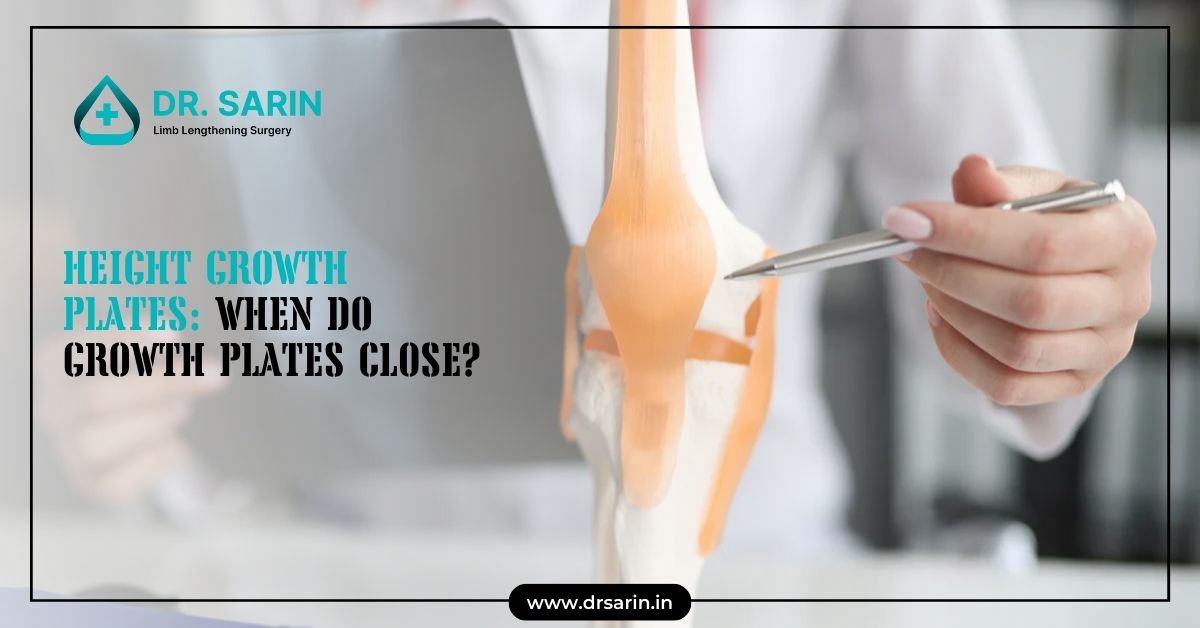
Growth or epiphyseal plates are areas of developing cartilage tissue near the ends of long bones. They are crucial during the growth and development phase
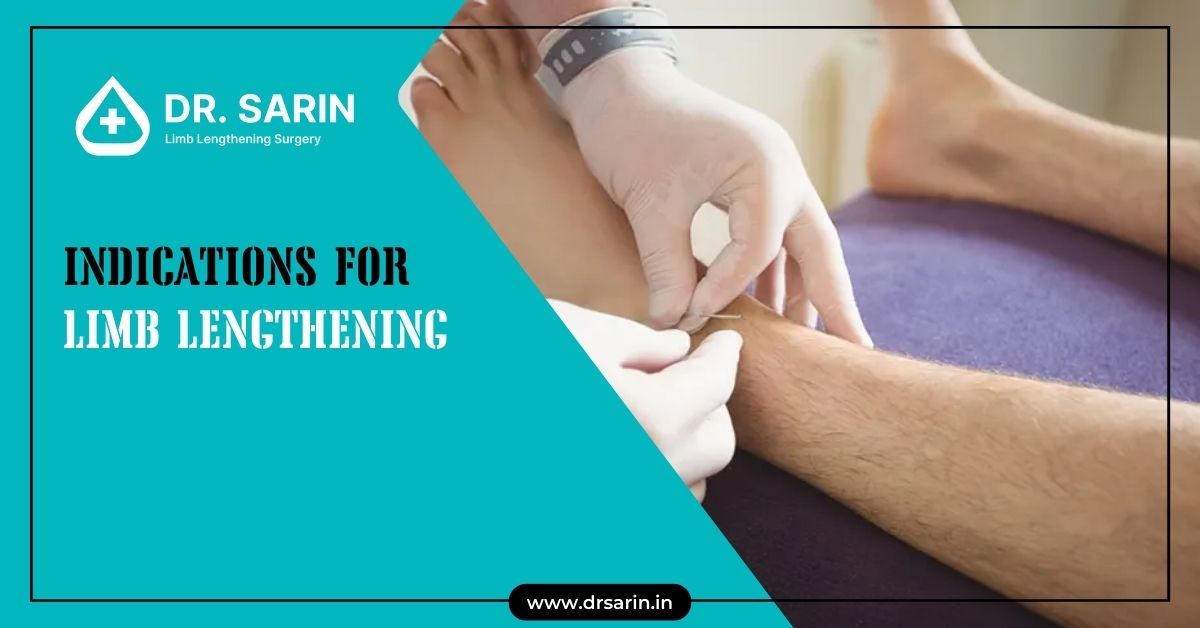
Limb lengthening is a surgical procedure designed to correct discrepancies in limb length, restore normal function, and improve the quality of life for patients with

Why Is Surgical Skin Preparation Important? Surgical skin preparation removes dirt, oil, and microorganisms from the skin’s surface. This process reduces the risk of postoperative
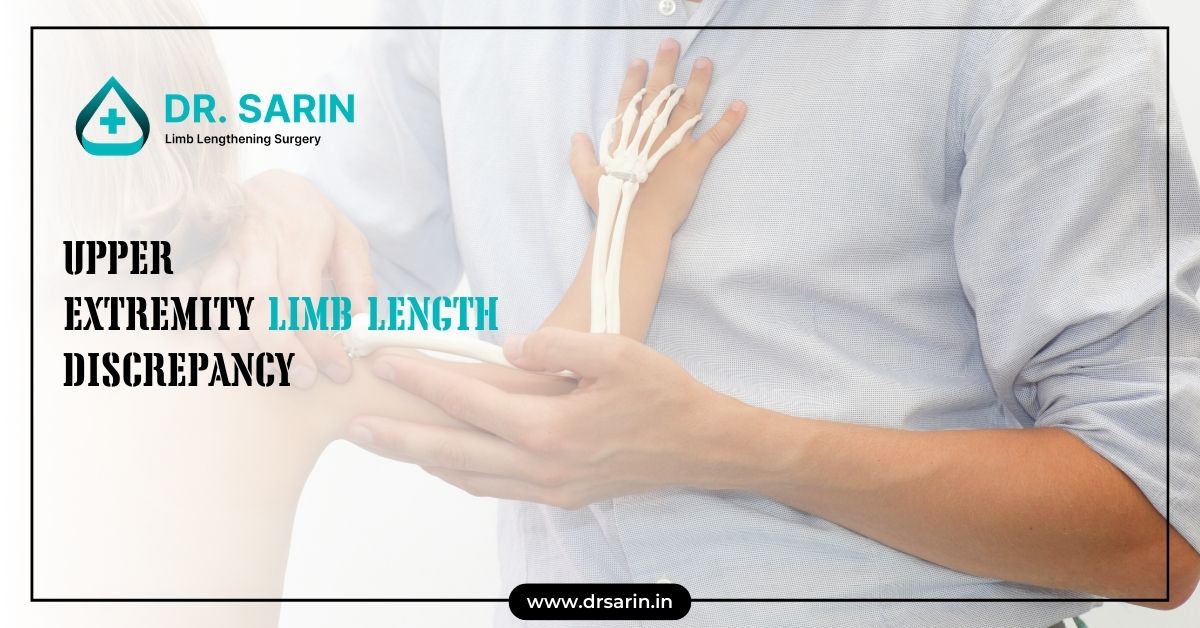
The upper extremity, comprising the arm, forearm, and hand, is a complex structure that facilitates a wide range of motions and functions. The skeletal anatomy

The surgery has become famous for those looking to increase their height. This procedure involves surgically lengthening the bones in the legs, allowing individuals to

Limb lengthening surgery is a complex procedure that involves the gradual extension of bones to correct discrepancies or enhance height. In India, the cost of
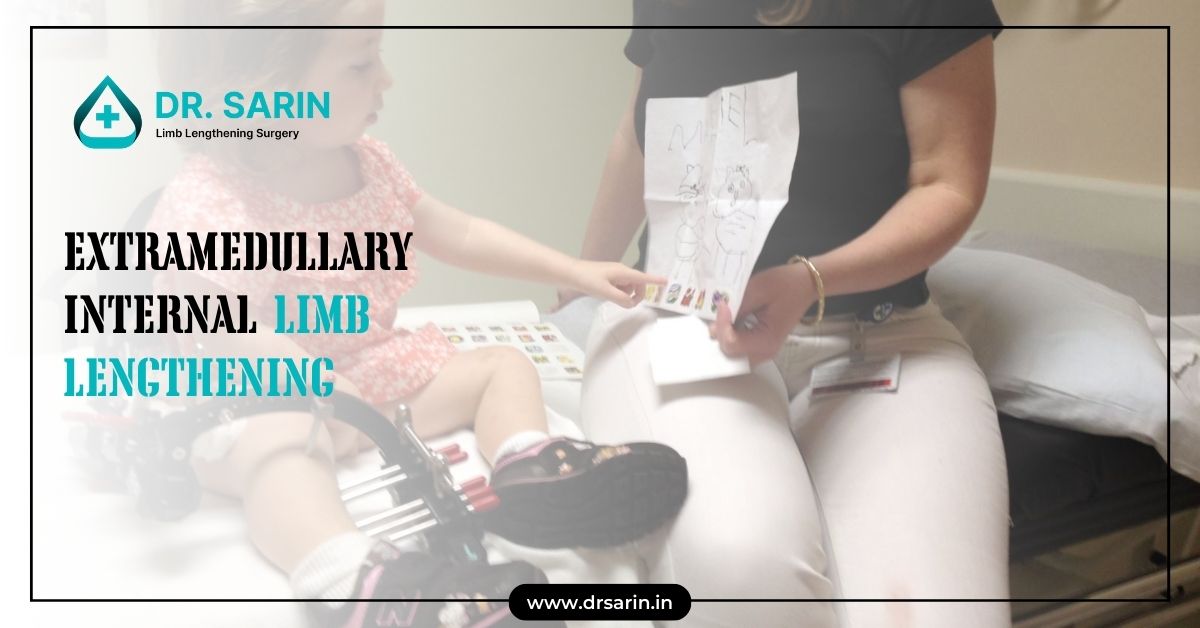
Abstract Extramedullary Internal Limb Lengthening (EMILL) represents an advanced surgical approach to address limb length discrepancies and deformities. This technique utilizes external devices and internal

Limb-lengthening is a complex orthopedic procedure that can significantly improve a person’s physical stature, correct deformities, or address discrepancies in limb length. However, while the

For years, it has been common for children to grow taller than their parents, especially in countries where living conditions, nutrition, and healthcare have improved.

Most people stop growing taller after the age of 18. But why does height increase stop at this point? Is there a biological cut-off, or
Limb lengthening surgery is a life-changing procedure that can dramatically improve physical appearance, posture, self-esteem, and even mobility in some cases. However, like any major
How Safe Is Limb Lengthening Surgery? Risks and Precautions This relatively recent surgical procedure has become a promise to many who want to augment the
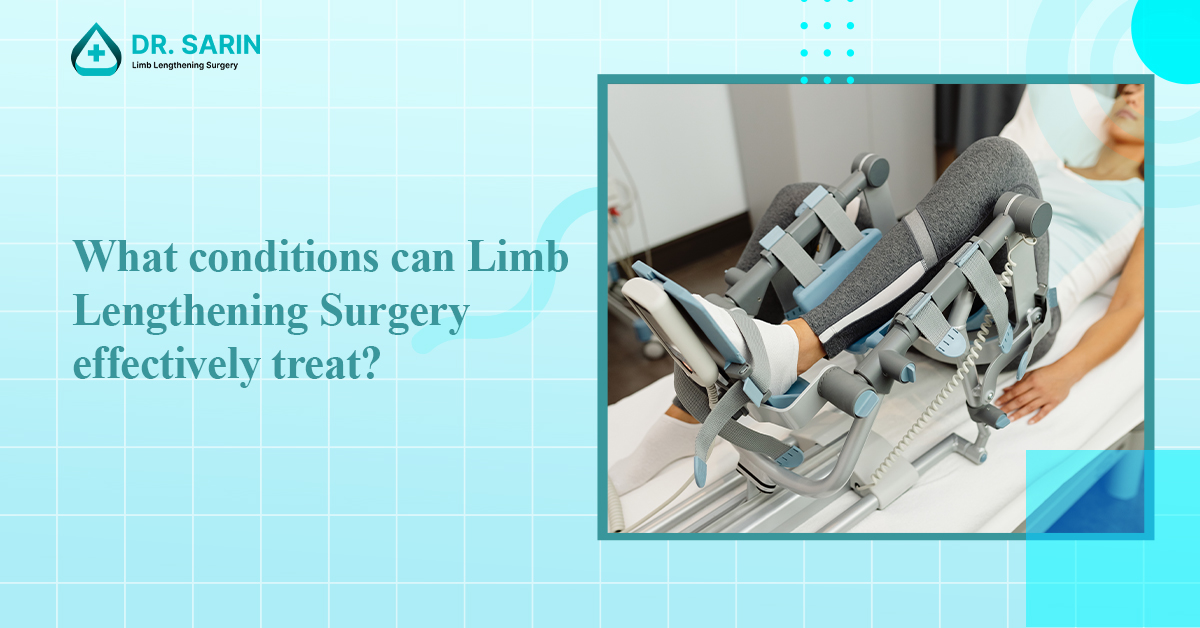
Limb lengthening surgery is a specialized orthopedic procedure used to increase the length of bones, typically in the legs or arms, and can effectively treat

Height Increase Surgery Complications: Understanding the Risks Involved in Limb Lengthening Procedures Height increase surgery—also known as limb lengthening surgery—has grown in popularity among individuals

Limb lengthening surgery has become a revolutionary procedure for individuals looking to increase their height. While the idea of growing taller through surgery may seem

Understanding Mogging and Its Impact on Height Perception In a world where physical appearance plays a significant role in personal and professional interactions, height often

Recovery after limb lengthening surgery is just as important as the procedure itself. Physical therapy and controlled exercise play a crucial role in helping patients

The average height of a population serves as a key indicator of overall health and nutrition levels within a country. In the UK, this metric

Limb Lengthening Surgery in India: Why International Patients Choose Dr. Sarin: In recent years, India has become a global hub for advanced medical treatments, including

In 2025, limb lengthening surgery is more advanced, safer, and in higher demand than ever. With innovations in medical technology, improved recovery timelines, and growing

In pursuing aesthetic balance and improved functionality, many individuals consider limb lengthening surgery. This transformative procedure, often sought after for various reasons, can greatly impact

Limb lengthening is a fascinating medical procedure that has gained popularity in recent years, offering hope to individuals with limb length discrepancies and other orthopedic
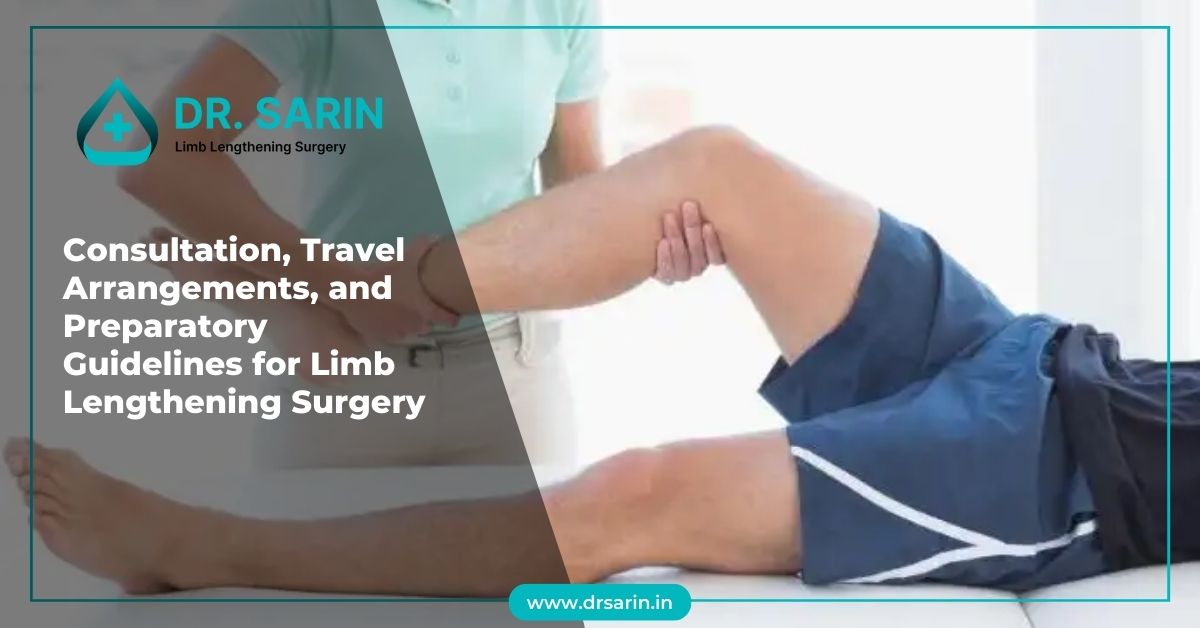
Limb lengthening surgery is a significant medical procedure that requires thorough preparation and planning. From the initial consultation to post-surgery recovery, every step of the
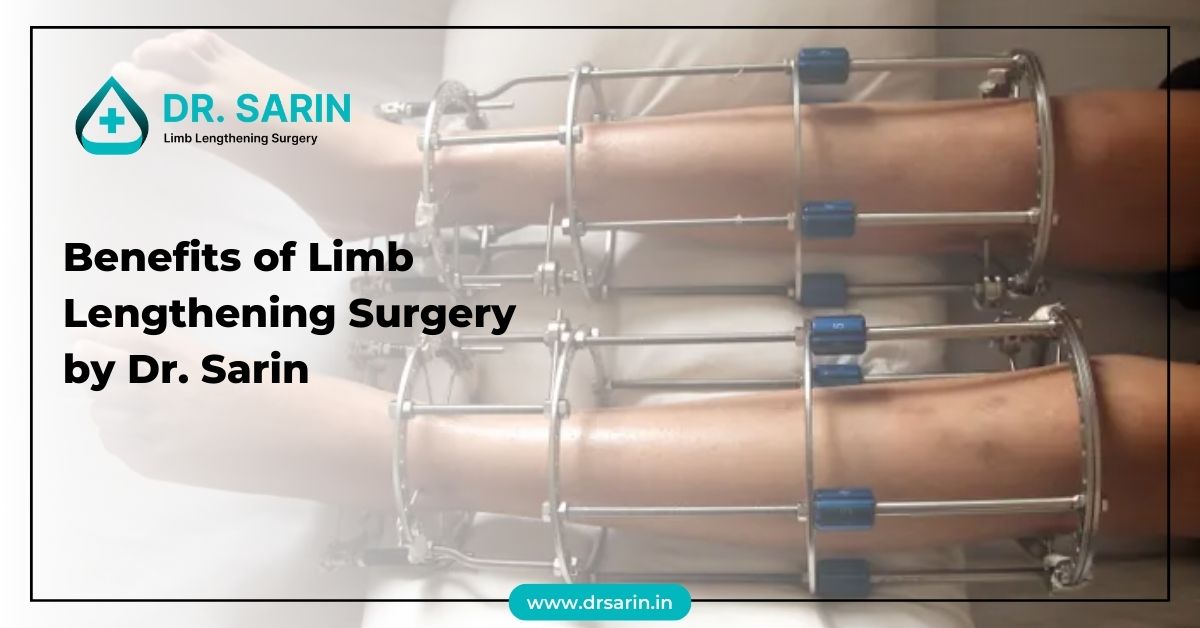
Limb lengthening surgery, a procedure designed to increase the length of limbs, offers hope and improved quality of life for individuals with limb length discrepancies

A successful limb lengthening surgery isn’t just about the operation-it’s also about what happens afterward. One of the most underrated yet powerful aspects of recovery

Yes, you can still run after height increase (limb lengthening) surgery, but only after a full recovery, which usually takes 6 to 12 months. With

Want to Know How to Lengthen Legs? Let’s be honest, many of us have looked in the mirror and wished we had longer legs. Whether
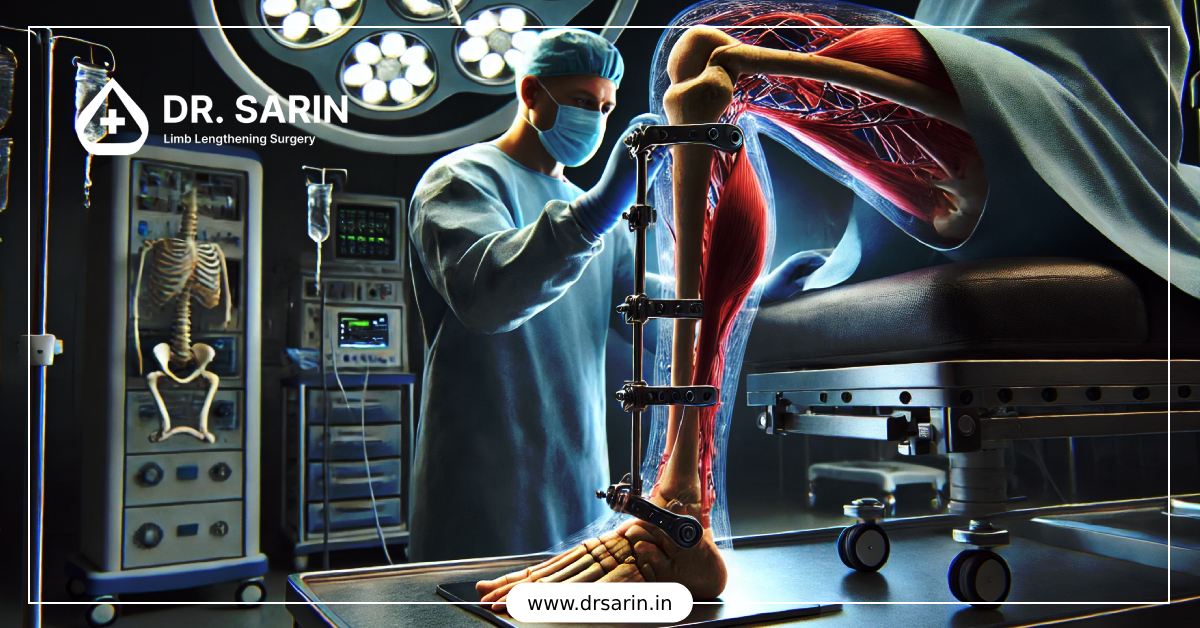
Limb lengthening surgery is a medical procedure designed to increase bone length, primarily in the legs. This surgery is commonly performed for individuals with limb

Leg lengthening surgery is a remarkable medical procedure that offers the potential for increased height or correction of limb deformities. While the surgery holds promising